-
N&PD Moderators: Skorpio | thegreenhand
-
Neuroscience & Pharmacology Discussion Welcome Guest
Posting Rules Bluelight Rules Recent Journal Articles Chemistry Mega-Thread FREE Chemistry Databases! Self-Education Guide
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Ketamine salts solubility
- Thread starter fastandbulbous
- Start date
Gaffy
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Oct 27, 2018
- Messages
- 1,210
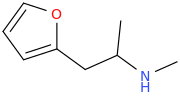
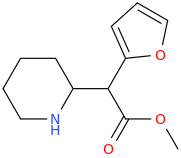
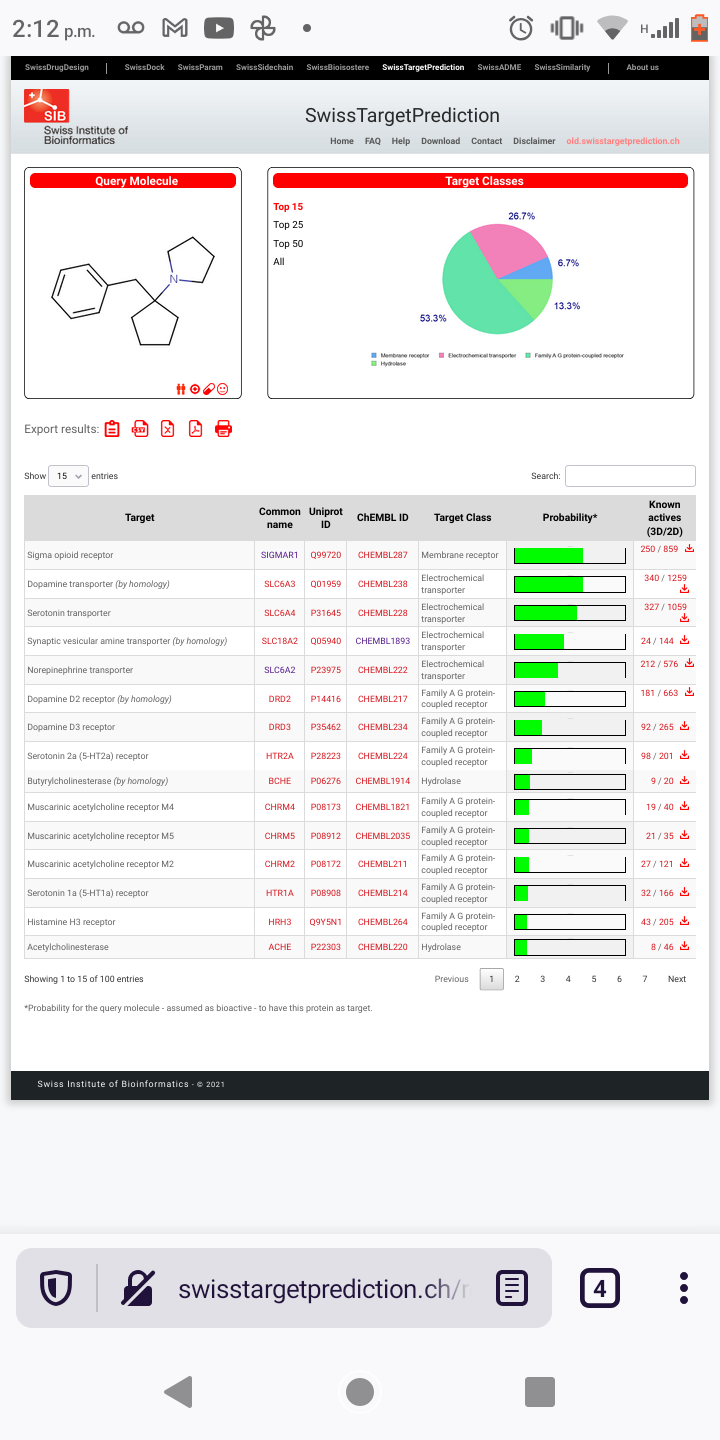
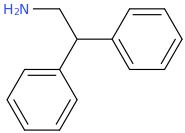
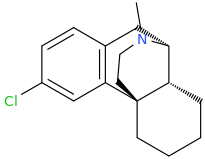
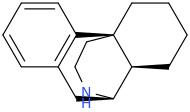
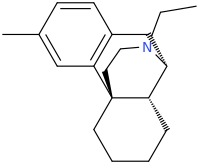
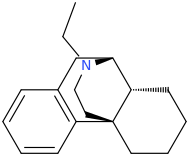
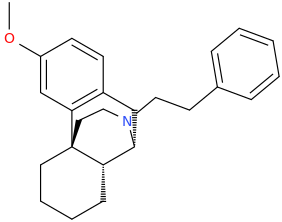
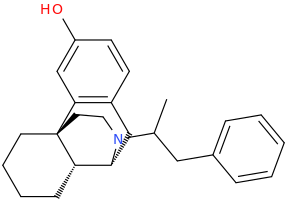
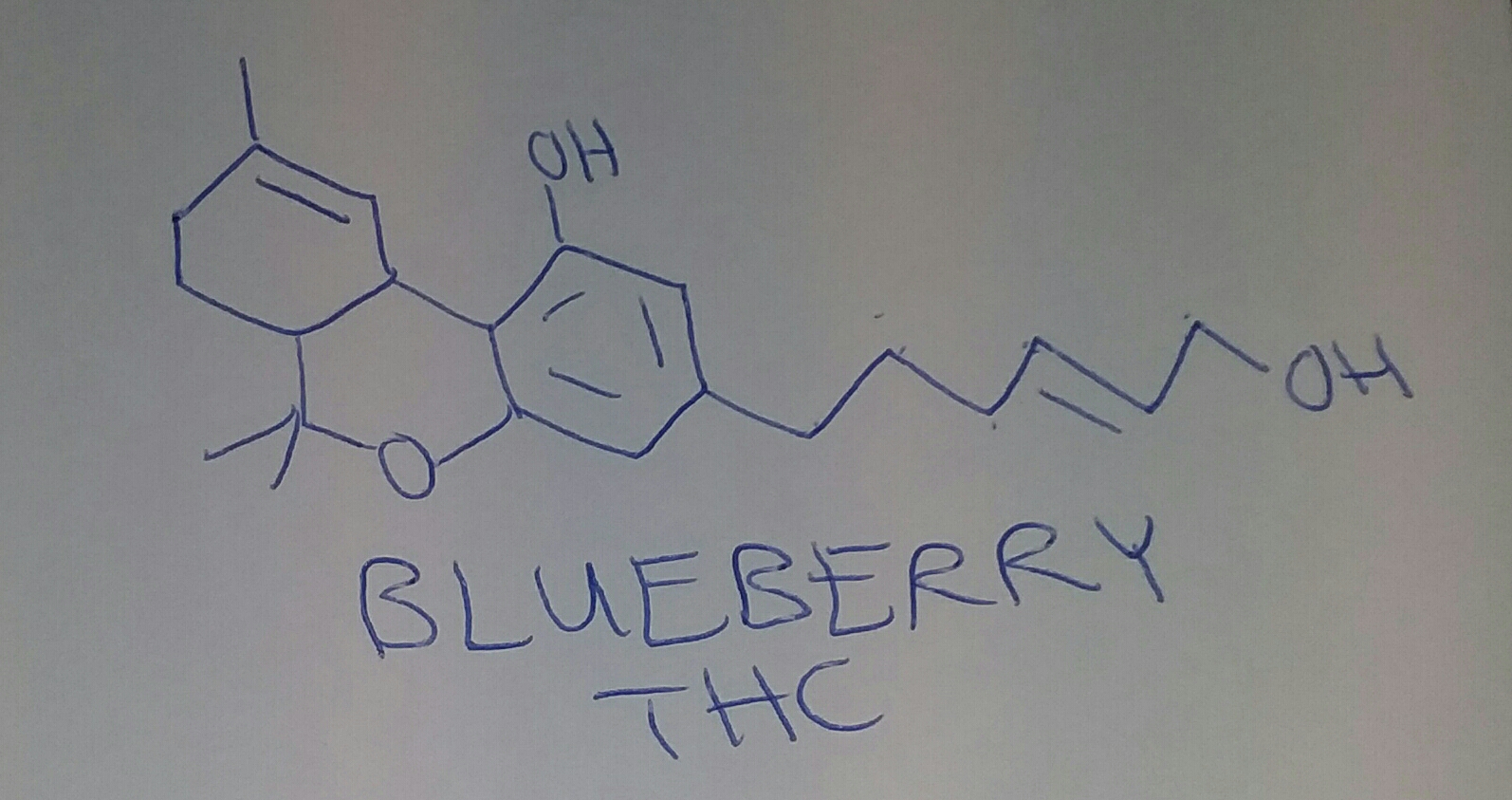
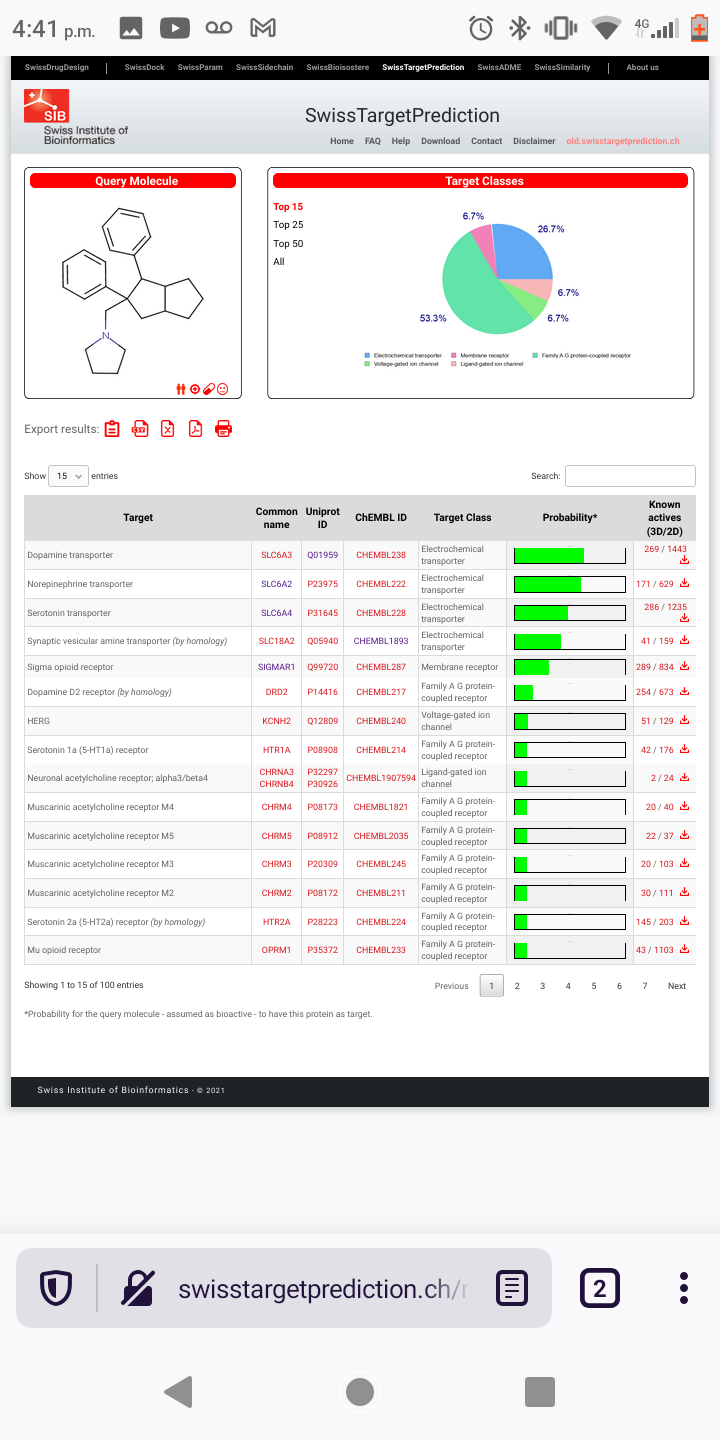
Just copy/past them into stpI don't know how to read Smiles.
Nagelfar
Bluelight Crew
- Joined
- Nov 23, 2007
- Messages
- 2,527
Brain Damage Linked to Common Compound In Everyday Plastic Items:
“Bisphenols exert detrimental effects on neuronal signaling in mature vertebrate brains” by Elisabeth Schirmer, Stefan Schuster & Peter Machnik. Communications Biology
Human Taste Buds Can Tell The Difference Between Normal And 'Heavy' Water
↑…and on a lighter note. Human taste-buds can distinguish deuterium from plain H²O.
“Bisphenols exert detrimental effects on neuronal signaling in mature vertebrate brains” by Elisabeth Schirmer, Stefan Schuster & Peter Machnik. Communications Biology
—The plasticizers contained in many everyday objects can impair important brain functions in humans. Biologists from the University of Bayreuth warn of this danger in an article in Communications Biology. Their study shows that even small amounts of the plasticizers bisphenol A and bisphenol S disrupt the transmission of signals between nerve cells in the brains of fish.
The researchers consider it very likely that similar interference can also occur in the brains of adult humans. They, therefore, call for the rapid development of alternative plasticizers that do not pose a risk to the central nervous system.
Bisphenols are plasticisers that are found in a large number of plastic products worldwide – for example, in food packaging, plastic tableware, drinking bottles, toys, tooth fillings, and babies’ dummies. In recent years, numerous health risks have already been associated with them, especially with bisphenol A (BPA).
The Bayreuth research team led by Dr. Peter Machnik at the Animal Physiology research group (led by Dr. Stefan Schuster) has now for the first time investigated the effects of plasticisers on signal transmission between nerve cells in the adult brain.
The study covers not only BPA, but also bisphenol S (BPS), which is often considered less harmful to health. Their findings: Both plasticisers impair communication between the nerve cells of the brain.
Permanent damage to the nervous system
The harmful effects on the brain mainly affect the delicate balance between different neuronal functions. While some brain cells transmit signals that trigger a state of excitation in downstream cells, other brain cells have the function of inhibiting downstream cells. However, the coordination of both excitation and inhibition is essential for an intact central nervous system.
“It is well known that numerous disorders in the nervous system of vertebrates are triggered by the fact that excitatory signals and inhibitory signals are not or only inadequately coordinated. So, it is all the more alarming that the plasticizers BPA and BPS significantly impair precisely this coordination,” explains Dr. Peter Machnik, lead author of the study.
“We were surprised how many vital brain functions in fish are affected by the plasticizers used in numerous industries. This damage, as we were able to show, does not occur immediately. However, when the brain cells are exposed to small amounts of BPA or BPS for a month, the damage is unmistakable,” says Elisabeth Schirmer, a doctoral student from Bayreuth and first author of the study.
It turns out that the plasticisers influence the action potential of brain cells. They alter the chemical and electrical transmission of signals through the synapses. In addition, they disrupt the circuits that are important for the perception and processing of acoustic and visual stimuli.
Studies on Mauthner cells in goldfish
The discovery of the damage caused by plasticizers came from detailed studies on live goldfish. The focus was on the two largest nerve cells in fish brain, the Mauthner cells. They integrate all sensory stimuli, all of which must be processed quickly and in a precisely coordinated manner when predators approach. In this case, the Mauthner cells trigger life-saving escape reactions.
Due to this function, which is essential for survival, they have become particularly robust in the course of evolution. Mauthner cells are able to ward off damaging influences to a certain extent, or to compensate for damage afterwards. This makes it all the more significant that plasticizers are able to cause considerable damage to these cells.
Transferability of the results to humans – Demand for alternative plasticisers
“The findings obtained through studies on fish brains justify the assessment that BPA and BPS can also seriously damage the brains of adult humans. Against this background, it is essential that science and industry develop new plasticizers to replace these bisphnols, while being safe for human health,” says Dr. Peter Machnik.
Prof. Dr. Stefan Schuster adds: “The efficiency of the research techniques we used in our study could, in addition, prove a valuable aid in the development of alternative plasticizers. They make it possible to quickly and inexpensively test how a substance under consideration affects brain cells.”
Bisphenols are important plasticizers currently in use and are released at rates of hundreds of tons each year into the biosphere. However, for any bisphenol it is completely unknown if and how it affects the intact adult brain, whose powerful homeostatic mechanisms could potentially compensate any effects bisphenols might have on isolated neurons.
Here we analyzed the effects of one month of exposition to BPA or BPS on an identified neuron in the vertebrate brain, using intracellular in vivo recordings in the uniquely suited Mauthner neuron in goldfish.
Our findings demonstrate an alarming and uncompensated in vivo impact of both BPA and BPS—at environmentally relevant concentrations—on essential communication functions of neurons in mature vertebrate brains and call for the rapid development of alternative plasticizers.
The speed and resolution of the assay we present here could thereby be instrumental to accelerate the early testing phase of next-generation plasticizers
Human Taste Buds Can Tell The Difference Between Normal And 'Heavy' Water
↑…and on a lighter note. Human taste-buds can distinguish deuterium from plain H²O.
- Joined
- May 11, 2011
- Messages
- 3,370
Brain Damage Linked to Common Compound In Everyday Plastic Items:
“Bisphenols exert detrimental effects on neuronal signaling in mature vertebrate brains” by Elisabeth Schirmer, Stefan Schuster & Peter Machnik. Communications Biology
—
Human Taste Buds Can Tell The Difference Between Normal And 'Heavy' Water
↑…and on a lighter note. Human taste-buds can distinguish deuterium from plain H²O.
That bisphenol study is interesting, as they used ethinyl estradiol as a control, and saw similar results. I am not sure what common exposure levels are when compared to the doses used in this study. They talk about the need for new plasticizers, I would be wary of anything with estrogen like bulk and a free phenol group. Unfortunately those phenols react well in plastics.
- Joined
- May 11, 2011
- Messages
- 3,370
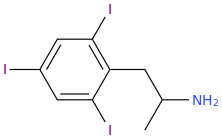
SHARON
1-cyclohexyl-2-ethylaminopropane
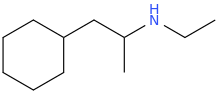
NOSAMULLI
des-oxo-LSD-025
SHARON -
For when benzedrex lacks enough norepinephrine punch!
Here's the secret what Alexander Shulgin didn't want you to know and love. Doctors hate this man!
izo
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Mar 22, 2006
- Messages
- 4,165
Passiflora Incarnata related:
Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 15;831:77-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 5.

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
J Ethnopharmacol. 1997 Jun;57(1):11-20.
doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(97)00042-1.

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Planta Med. 2008 Dec;74(15):1769-73.
doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1088322. Epub 2008 Nov 12.

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
would be nice if anyone has access and can get them...
edit: just saw that this thread is just about recent articles, sorry. hope that somebody can help nevertheless.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 15;831:77-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 5.
Flavones-bound in benzodiazepine site on GABA A receptor: Concomitant anxiolytic-like and cognitive-enhancing effects produced by Isovitexin and 6-C-glycoside-Diosmetin

Flavones-bound in benzodiazepine site on GABAA receptor: Concomitant anxiolytic-like and cognitive-enhancing effects produced by Isovitexin and 6-C-glycoside-Diosmetin - PubMed
Increasing evidence suggests that flavones can modulate memory and anxiety-like behaviour. However, these therapeutic effects are inconsistent and induce of adverse effects, which have been associated with interactions at the Benzodiazepine (BZ)-binding site. To improve our understanding of...
Abstract
Increasing evidence suggests that flavones can modulate memory and anxiety-like behaviour. However, these therapeutic effects are inconsistent and induce of adverse effects, which have been associated with interactions at the Benzodiazepine (BZ)-binding site. To improve our understanding of flavone effects on memory and anxiety, we employed a plus-maze discriminative avoidance task. Furthermore, we evaluated the potential of the compounds in modulating GABAA receptors via BZ-binding site using molecular modelling studies. Adult male Wistar rats were treated 30 min before training session with Vicenin-2 (0.1 and 0.25 mg/kg), Vitexin (0.1 and 0.25 mg/kg), Isovitexin (0.1 and 0.25 mg/kg) and 0.1 mg/kg 6-C-glycoside-Diosmetin, vehicle and a GABAA receptor agonist. The analysis of the time spent in the non-aversive vs aversive enclosed arms during the test session and percentage of time in the open arms within the training session revealed that treatment with Isovitexin and 6-C-glycoside-Diosmetin had memory-enhancing and anxiolytic-like effects (P < 0.001). In contrast, treatment with a higher dose of Diazepam impaired short-and long-term memory when it alleviated anxiety level. Docking studies revealed that flavones docked in a very similar way to that observed to the Diazepam, except by a lack of interaction in residue α1His101 in the BZ-binding site on GABAA receptors, which may be related to memory-enhancing effect. The occurrence of the α1His101 interaction could justify the memory-impairing observed following Diazepam treatment. These findings provide the first evidence that Isovitexin and 6-C-glycoside-Diosmetin could exert their memory-enhancing and anxiolytic-like effects via GABAA receptor modulation, which likely occurs via their benzodiazepine-binding site.
J Ethnopharmacol. 1997 Jun;57(1):11-20.
doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(97)00042-1.
Behavioural effects of Passiflora incarnata L. and its indole alkaloid and flavonoid derivatives and maltol in the mouse

Behavioural effects of Passiflora incarnata L. and its indole alkaloid and flavonoid derivatives and maltol in the mouse - PubMed
Lyophilised hydroalcoholic and aqueous extracts of the aerial parts of Passiflora incarnata L. (Passifloraceae) (Passion-flower), as well as chemical constituents of the plant, indole alkaloids (harman, harmin, harmalin, harmol, and harmalol) maltol and flavonoids (orientin, isoorientin, vitexin...
Abstract
Lyophilised hydroalcoholic and aqueous extracts of the aerial parts of Passiflora incarnata L. (Passifloraceae) (Passion-flower), as well as chemical constituents of the plant, indole alkaloids (harman, harmin, harmalin, harmol, and harmalol) maltol and flavonoids (orientin, isoorientin, vitexin and isovitexin) were assessed for behavioral effects in mice. The accordance with the traditional use of P. incarnata, psychotropic properties were confirmed by some behavioral tests in mice. The anxiolytic properties of hydroalcoholic extract were confirmed at 400 mg/kg by the increase of rears and steps climbed in the staircase test (non-familiar environmental test), and the increase in locomotion and time spent in light side in the light/dark box choice test (non-familiar environmental test). The sedative properties of aqueous extract were confirmed at 400 g/kg by decrease of rears and steps climbed in the staircase test and the decrease of rears and locomotion in the free exploratory test. Moreover, the aqueous extract induced sleep in mice after treatment with a sub-hypnotic dose of pentobarbital.
Planta Med. 2008 Dec;74(15):1769-73.
doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1088322. Epub 2008 Nov 12.
Anxiolytic activity of a phytochemically characterized Passiflora incarnata extract is mediated via the GABAergic system

Anxiolytic activity of a phytochemically characterized Passiflora incarnata extract is mediated via the GABAergic system - PubMed
The purpose of this research was to assess the anxiolytic properties of a phytochemically characterized commercial extract from Passiflora incarnata (PI; Passifloraceae) in the elevated plus maze test in mice. Using an HPLC method, the flavonoids homoorientin, orientin, vitexin, and isovitexin...
Abstract
The purpose of this research was to assess the anxiolytic properties of a phytochemically characterized commercial extract from Passiflora incarnata (PI; Passifloraceae) in the elevated plus maze test in mice. Using an HPLC method, the flavonoids homoorientin, orientin, vitexin, and isovitexin were identified as major compounds. Following oral administration, the extract exerted an anxiolytic effect that was comparable to diazepam (1.5 mg/kg) at a dose of 375 mg/kg and exhibited a U-shaped dose-response curve. In addition, antagonism studies using the GABA (A)/benzodiazepine receptor antagonist flumazenil and the 5-HT (1A)-receptor antagonist WAY-100 635 were conducted. The active dose was effectively antagonized by flumazenil, but not by WAY-100 635. This study is the first demonstration of the IN VIVO, GABA-mediated anxiolytic activity of an HPLC- characterized extract of Passiflora incarnata.
would be nice if anyone has access and can get them...
edit: just saw that this thread is just about recent articles, sorry. hope that somebody can help nevertheless.
Last edited:
- Joined
- May 11, 2011
- Messages
- 3,370
would be nice if anyone has access and can get them...
Do you know how to upload pdfs?
Alternately you can use scihub (the scihub.se link just worked for me, but I usually Google it so I can find current links). I had to use it to get the third paper.
izo
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Mar 22, 2006
- Messages
- 4,165
Do you know how to upload pdfs?
if i remember correctly upload for files is disabled now on bluelight.
- Joined
- May 11, 2011
- Messages
- 3,370
if i remember correctly upload for files is disabled now on bluelight.
The go the scihub route.