-
Neuroscience & Pharmacology Discussion Welcome Guest
Posting Rules Bluelight Rules Recent Journal Articles Chemistry Mega-Thread FREE Chemistry Databases! Self-Education Guide -
N&PD Moderators: Skorpio | someguyontheinternet
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Ketamine salts solubility
- Thread starter fastandbulbous
- Start date
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
I'LL FEEL'T-TRIP
n-monomethyl-ALpha PHenYL'TRYPtamine
SwissTargetPrediction
MEOWTWO
SwissTargetPrediction
MEOWTWO GOLD
Last edited:
Has anyone considered that different enantiomers of a chiral compound have different actions. AMT is a good example. When resolved, only 1 isomer has 5HT2a affinity, the other is just stimulating. I suspect that 6,a-DMT would produce entactogenic activity. 6,a,a,-TMT (achiral) is another interesting one.
Actually I'm quite tweaked and am trying to figure it out for FACAP, 4F-Phenyl-1-CycloPentyl-(2-Methyleminate) and can't select chirals on my mobile phone on STP. Would you point it out with this given example?Has anyone considered that different enantiomers of a chiral compound have different actions. AMT is a good example. When resolved, only 1 isomer has 5HT2a affinity, the other is just stimulating. I suspect that 6,a-DMT would produce entactogenic activity. 6,a,a,-TMT (achiral) is another interesting one.
Actually I'm quite tweaked and am trying to figure it out for FACAP, 4F-Phenyl-1-CycloPentyl-(2-Methyleminate) and can't select chirals on my mobile phone on STP. Would you point it out with this given example?
STP = DOM? Yes. That would be an excellent example. The example I would really like to test is DON. 2CN is described as 'tofu' and I suspect (R) DON would be similar. You will note that the PEAs are part of the structure of LSD. I HAVE tried the optically resolved AMT but mechanical losses made it expensive. If one was to make 6-methyl AMT, the 6-Me would provide a convenient 'metabolic handle' for the liver to oxidize and thus remove the metabolite. The PEAs & tryptamines overly with the para position of the PEAs overlaying the 6-position of tryptamines. I suggested to Dr. Dave that 3-Me LSD might be interesting and although interested, he baulked at the synthesis.
So often we think about compounds that will never be made due to the complexity of the synthesis. If I mention something, either I HAVE made it or I know someone who HAS made it. I have poor lab technique so I limit myself to working out synthetic pathways. I think it's important to admit one's limitations.
But yeah.... great example. Of course, there are a limited number of synthetic pathways. There IS a supplier in the UK that allows one to obtain the appropriate nitroalkene/nitroalkane so 1 or 2 (2 is still possibly 1 pot) steps.
sekio
Bluelight Crew
The odor of street cocaine and the compound that dogs will respond to is not cocaine itself, but rather methyl benzoate formed by transesterifcation.
There is actually a patent: US4260517A - Available aroma of cocaine.
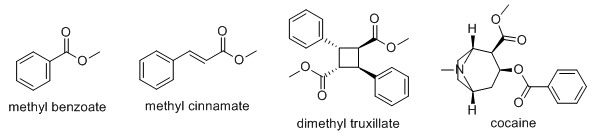
Now you can formulate a perfume that smells like Peruvian flake. And, as a bonus, you can make life hard for anyone who passes by a drug-sniffing dog (maybe useful as a diverting tactic).
I find it interesting that Sigma apparently sells a synthetic cocaine odorant to train police dogs on. My money's on it being the above composition.
Bonus questions for the curious (my answers below):
1. Why does high quality cocaine contain mostly methyl benzoate?
2. How does truxillic acid form?
There is actually a patent: US4260517A - Available aroma of cocaine.
When methyl benzoate is volatilized and then highly diluted with a gaseous non-odor masking diluent, the aroma of cocaine is provided. Similarly, when a mixture of methyl benzoate, methyl cinnamate and the dimethyl ester of truxillic acid is volatilized and then highly diluted with a gaseous non-odor masking diluent, the aroma of various grades of "street cocaine" is provided.
A unique feature of the present invention is that the aroma of cocaine is not merely imitated, but rather, the actual aroma of cocaine is provided without the use of any cocaine or cocaine related materials. Since the actual aroma of cocaine is provided by the present invention, it is possible to use the present invention to establish a chemical model for the aroma of cocaine. This chemical model may then be used in various qualitative and quantitative analytical techniques.

Now you can formulate a perfume that smells like Peruvian flake. And, as a bonus, you can make life hard for anyone who passes by a drug-sniffing dog (maybe useful as a diverting tactic).
I find it interesting that Sigma apparently sells a synthetic cocaine odorant to train police dogs on. My money's on it being the above composition.
Bonus questions for the curious (my answers below):
1. Why does high quality cocaine contain mostly methyl benzoate?
2. How does truxillic acid form?
NSFW:
1. The oxidation with permanganate would destroy the truxillic acids & cinnamic acids
2. Photochemical dimerization! Two molecules of cinnamic acid will couple together.
2. Photochemical dimerization! Two molecules of cinnamic acid will couple together.
Last edited:
sekio
Bluelight Crew
journal dump
Bis(4-hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptammonium) fumarate: a new crystalline form of miprocin
Andrew R. Chadeayne,a* Duyen N. K. Pham,b James A. Golenb and David R. Mankeb
The title compound, bis(4-hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptammonium) (4-HO-MiPT) fumarate (systematic name: bis{[2-(4-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl](methyl)propan-2-ylazanium} but-2-enedioate), 2C14H21N2O+·C4H2O42−, has a singly protonated tryptammonium cation and one half of a fumarate dianion in the asymmetric unit. The tryptammonium and fumarate ions are held together in one-dimensional chains by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. [...]
Terpenoids Commonly Found in Cannabis sativa Do Not Modulate the Actions of Phytocannabinoids or Endocannabinoids on TRPA1 and TRPV1 Channels
Marika Heblinski, Marina Santiago, Charlotte Fletcher, Jordyn Stuart, Mark Connor, Iain S. McGregor, and Jonathon C. Arnold
Published Online:9 Mar 2020
Results: α-pinene, β-pinene, β-caryophyllene, linalool, limonene, β-myrcene or α-humulene did not affect [Ca]i in hTRPA1 and hTRPV1 overexpressing cells. Cinnamaldehyde (CA), Δ9-THC, and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) activated TRPA1 receptors with high efficacy and similar potency (EC50s of ∼10 μM). Capsaicin and anandamide (AEA) activated TRPV1 receptors with an EC50 of 61 nM and 4.3 μM, respectively, but TRPV1 showed no response to Δ9-THC, cannabidiol, and other minor cannabinoids. Terpenoids did not significantly affect the responses of TRPA1 and TRPV1 receptors to submaximal and maximal concentrations of CA and Δ9-THC or the endocannabinoids AEA and 2-AG.
Discussion: We could not find any evidence that the terpenoids tested here activate TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels or modulate their activation by Δ9-THC and other agonists, including endocannabinoids.
Potential for release of pulmonary toxic ketene from vaping pyrolysis of vitamin E acetate
Dan Wu and View ORCID ProfileDonal F. O’Shea
PNAS March 24, 2020 117 (12) 6349-6355; first published March 10, 2020
Abstract
A combined analytical, theoretical, and experimental study has shown that the vaping of vitamin E acetate has the potential to produce exceptionally toxic ketene gas, which may be a contributing factor to the upsurge in pulmonary injuries associated with using e-cigarette/vaping products. Additionally, the pyrolysis of vitamin E acetate also produces carcinogen alkenes and benzene for which the negative long-term medical effects are well recognized. As temperatures reached in vaping devices can be equivalent to a laboratory pyrolysis apparatus, the potential for unexpected chemistries to take place on individual components within a vape mixture is high. Educational programs to inform of the danger are now required, as public perception has grown that vaping is not harmful.
Br J Anaesth. 2018 Jul;121(1):260-269. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 May 10.
Dreaming and awareness during dexmedetomidine- and propofol-induced unresponsiveness.
Radek L1, Kallionpää RE2, Karvonen M3, Scheinin A4, Maksimow A5, Långsjö J6, Kaisti K7, Vahlberg T8, Revonsuo A9, Scheinin H10, Valli K11.
BACKGROUND:
Experiences during anaesthetic-induced unresponsiveness have previously been investigated by interviews after recovery. To explore whether experiences occur during drug administration, we interviewed participants during target-controlled infusion (TCI) of dexmedetomidine or propofol and after recovery.
METHODS:
Healthy participants received dexmedetomidine (n=23) or propofol (n=24) in stepwise increments until loss of responsiveness (LOR1). During TCI we attempted to arouse them for interview (return of responsiveness, ROR1). After the interview, if unresponsiveness ensued with the same dose (LOR2), the procedure was repeated (ROR2). Finally, the concentration was increased 1.5-fold to achieve presumable loss of consciousness (LOC), infusion terminated, and the participants interviewed upon recovery (ROR3). An emotional sound stimulus was presented during LORs and LOC, and memory for stimuli was assessed with recognition task after recovery. Interview transcripts were content analysed.
RESULTS:
Of participants receiving dexmedetomidine, 18/23 were arousable from LOR1 and LOR2. Of participants receiving propofol, 10/24 were arousable from LOR1 and two of four were arousable from LOR2. Of 93 interviews performed, 84% included experiences from periods of unresponsiveness (dexmedetomidine 90%, propofol 74%). Internally generated experiences (dreaming) were present in 86% of reports from unresponsive periods, while externally generated experiences (awareness) were rare and linked to brief arousals. No within drug differences in the prevalence or content of experiences during infusion vs after recovery were observed, but participants receiving dexmedetomidine reported dreaming and awareness more often. Participants receiving dexmedetomidine recognised the emotional sounds better than participants receiving propofol (42% vs 15%), but none reported references to sounds spontaneously.
CONCLUSION:
Anaesthetic-induced unresponsiveness does not induce unconsciousness or necessarily even disconnectedness.
Bis(4-hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptammonium) fumarate: a new crystalline form of miprocin
Andrew R. Chadeayne,a* Duyen N. K. Pham,b James A. Golenb and David R. Mankeb
The title compound, bis(4-hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-methyltryptammonium) (4-HO-MiPT) fumarate (systematic name: bis{[2-(4-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl](methyl)propan-2-ylazanium} but-2-enedioate), 2C14H21N2O+·C4H2O42−, has a singly protonated tryptammonium cation and one half of a fumarate dianion in the asymmetric unit. The tryptammonium and fumarate ions are held together in one-dimensional chains by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. [...]
Terpenoids Commonly Found in Cannabis sativa Do Not Modulate the Actions of Phytocannabinoids or Endocannabinoids on TRPA1 and TRPV1 Channels
Marika Heblinski, Marina Santiago, Charlotte Fletcher, Jordyn Stuart, Mark Connor, Iain S. McGregor, and Jonathon C. Arnold
Published Online:9 Mar 2020
Results: α-pinene, β-pinene, β-caryophyllene, linalool, limonene, β-myrcene or α-humulene did not affect [Ca]i in hTRPA1 and hTRPV1 overexpressing cells. Cinnamaldehyde (CA), Δ9-THC, and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) activated TRPA1 receptors with high efficacy and similar potency (EC50s of ∼10 μM). Capsaicin and anandamide (AEA) activated TRPV1 receptors with an EC50 of 61 nM and 4.3 μM, respectively, but TRPV1 showed no response to Δ9-THC, cannabidiol, and other minor cannabinoids. Terpenoids did not significantly affect the responses of TRPA1 and TRPV1 receptors to submaximal and maximal concentrations of CA and Δ9-THC or the endocannabinoids AEA and 2-AG.
Discussion: We could not find any evidence that the terpenoids tested here activate TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels or modulate their activation by Δ9-THC and other agonists, including endocannabinoids.
Potential for release of pulmonary toxic ketene from vaping pyrolysis of vitamin E acetate
Dan Wu and View ORCID ProfileDonal F. O’Shea
PNAS March 24, 2020 117 (12) 6349-6355; first published March 10, 2020
Abstract
A combined analytical, theoretical, and experimental study has shown that the vaping of vitamin E acetate has the potential to produce exceptionally toxic ketene gas, which may be a contributing factor to the upsurge in pulmonary injuries associated with using e-cigarette/vaping products. Additionally, the pyrolysis of vitamin E acetate also produces carcinogen alkenes and benzene for which the negative long-term medical effects are well recognized. As temperatures reached in vaping devices can be equivalent to a laboratory pyrolysis apparatus, the potential for unexpected chemistries to take place on individual components within a vape mixture is high. Educational programs to inform of the danger are now required, as public perception has grown that vaping is not harmful.
Br J Anaesth. 2018 Jul;121(1):260-269. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 May 10.
Dreaming and awareness during dexmedetomidine- and propofol-induced unresponsiveness.
Radek L1, Kallionpää RE2, Karvonen M3, Scheinin A4, Maksimow A5, Långsjö J6, Kaisti K7, Vahlberg T8, Revonsuo A9, Scheinin H10, Valli K11.
BACKGROUND:
Experiences during anaesthetic-induced unresponsiveness have previously been investigated by interviews after recovery. To explore whether experiences occur during drug administration, we interviewed participants during target-controlled infusion (TCI) of dexmedetomidine or propofol and after recovery.
METHODS:
Healthy participants received dexmedetomidine (n=23) or propofol (n=24) in stepwise increments until loss of responsiveness (LOR1). During TCI we attempted to arouse them for interview (return of responsiveness, ROR1). After the interview, if unresponsiveness ensued with the same dose (LOR2), the procedure was repeated (ROR2). Finally, the concentration was increased 1.5-fold to achieve presumable loss of consciousness (LOC), infusion terminated, and the participants interviewed upon recovery (ROR3). An emotional sound stimulus was presented during LORs and LOC, and memory for stimuli was assessed with recognition task after recovery. Interview transcripts were content analysed.
RESULTS:
Of participants receiving dexmedetomidine, 18/23 were arousable from LOR1 and LOR2. Of participants receiving propofol, 10/24 were arousable from LOR1 and two of four were arousable from LOR2. Of 93 interviews performed, 84% included experiences from periods of unresponsiveness (dexmedetomidine 90%, propofol 74%). Internally generated experiences (dreaming) were present in 86% of reports from unresponsive periods, while externally generated experiences (awareness) were rare and linked to brief arousals. No within drug differences in the prevalence or content of experiences during infusion vs after recovery were observed, but participants receiving dexmedetomidine reported dreaming and awareness more often. Participants receiving dexmedetomidine recognised the emotional sounds better than participants receiving propofol (42% vs 15%), but none reported references to sounds spontaneously.
CONCLUSION:
Anaesthetic-induced unresponsiveness does not induce unconsciousness or necessarily even disconnectedness.
polymath
Bluelight Crew
Potential for release of pulmonary toxic ketene from vaping pyrolysis of vitamin E acetate
Dan Wu and View ORCID ProfileDonal F. O’Shea
PNAS March 24, 2020 117 (12) 6349-6355; first published March 10, 2020
Abstract
A combined analytical, theoretical, and experimental study has shown that the vaping of vitamin E acetate has the potential to produce exceptionally toxic ketene gas, which may be a contributing factor to the upsurge in pulmonary injuries associated with using e-cigarette/vaping products. Additionally, the pyrolysis of vitamin E acetate also produces carcinogen alkenes and benzene for which the negative long-term medical effects are well recognized. As temperatures reached in vaping devices can be equivalent to a laboratory pyrolysis apparatus, the potential for unexpected chemistries to take place on individual components within a vape mixture is high. Educational programs to inform of the danger are now required, as public perception has grown that vaping is not harmful.
Looks like this chemical is about as toxic as fluorine gas according to some estimates.
Ketene - IDLH | NIOSH | CDC
The revised IDLH for ketene is 5 ppm based on acute inhalation toxicity data in humans and animals
Last edited:
The image isn't showing. ^^
Does this come close to Clubcard's ?:
 swisstargetprediction.ch
swisstargetprediction.ch
It's a carbon and a methoxy away from polymath's
Found it ( I think) :
VIP
Wipped cream, la crème de la crème.
A dedication to Clubcard
5ELO
La MD c'est pour les connards./ DPC
Un clin d'œil ;
A dedication to Sekio
BEASTMODE
A dedication to Polymath and its funny little beast, Phenmertine
Does this come close to Clubcard's ?:
SwissTargetPrediction
It's a carbon and a methoxy away from polymath's
Found it ( I think) :
VIP
Wipped cream, la crème de la crème.
A dedication to Clubcard
5ELO
La MD c'est pour les connards./ DPC
Un clin d'œil ;
A dedication to Sekio
BEASTMODE
A dedication to Polymath and its funny little beast, Phenmertine
Last edited:
polymath
Bluelight Crew
The laurus nobilis essential oil, which contains much the same terpenes as rosemary oil, has some antiviral effect against the previous SARS coronavirus that caused an epidemic in 2002-2003. Not to mean that it would be effective enough in practice to be worth it, but quite unexpected anyway.

 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

Phytochemical analysis and in vitro antiviral activities of the essential oils of seven Lebanon species - PubMed
The chemical composition of the essential oils of Laurus nobilis, Juniperus oxycedrus ssp. oxycedrus, Thuja orientalis, Cupressus sempervirens ssp. pyramidalis, Pistacia palaestina, Salvia officinalis, and Satureja thymbra was determined by GC/MS analysis. Essential oils have been evaluated for...
sekio
Bluelight Crew
Ketene gas is not only super toxic, about as toxic as phosgene, but it's also very reactive and flammable. One old school means of preparing acetic anhydride was by means of a 'ketene lamp' - a sealed glass apparatus where acetone vapor is drawn over a hot nichrome wire, pyrolysing it to methane and ketene, the latter of which reacts with glacial acetic acid to form acetic anhydride. A lab-scale generator can do 40 grams of acetic anhydride an hour, I'm told.
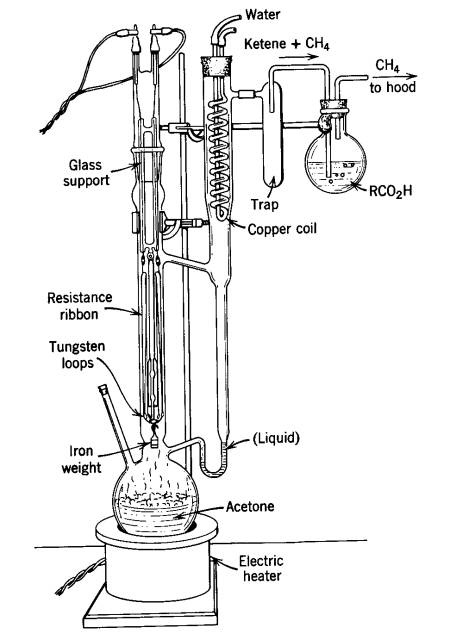
If you ask me, it's a death trap. The obvious hazard presented by bringing flammable vapors in contact with extreme heat, means rigorous exclusion of the atmosphere and any oxygen is a must. A good thick blast shield wouldn't be too much PPE.
I'm amazed that anyone managed to do this process and survive. For whatever reason, it was deemed reliable enough to be included in Vogel. There is even a related synthesis in OrgSyn using acetone vapor passed through a packed tube heated over open flame....
In chemistry news,
First steps towards a stable neon compound: observation and bonding analysis of [B12(CN)11Ne]−
Abstract
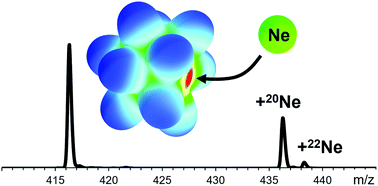
Noble gas (Ng) containing molecular anions are much scarcer than Ng containing cations. No neon containing anion has been reported so far. Here, the experimental observation of the molecular anion [B12(CN)11Ne]− and a theoretical analysis of the boron–neon bond is reported.
Talk about an unfavorable bond. I'm suprised.
NSFW:

If you ask me, it's a death trap. The obvious hazard presented by bringing flammable vapors in contact with extreme heat, means rigorous exclusion of the atmosphere and any oxygen is a must. A good thick blast shield wouldn't be too much PPE.
I'm amazed that anyone managed to do this process and survive. For whatever reason, it was deemed reliable enough to be included in Vogel. There is even a related synthesis in OrgSyn using acetone vapor passed through a packed tube heated over open flame....
In chemistry news,
First steps towards a stable neon compound: observation and bonding analysis of [B12(CN)11Ne]−
Abstract
Noble gas (Ng) containing molecular anions are much scarcer than Ng containing cations. No neon containing anion has been reported so far. Here, the experimental observation of the molecular anion [B12(CN)11Ne]− and a theoretical analysis of the boron–neon bond is reported.
Talk about an unfavorable bond. I'm suprised.
sekio
Bluelight Crew
Metab Eng. 2020 Mar 26. pii: S1096-7176(19)30401-X. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2019.12.007. [Epub ahead of print]
Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of psilocybin and related tryptamine derivatives.
Milne N, Thomsen P, Knudsen NM, Rubaszka P, Kristensen M, Borodina I.
Psilocybin is a tryptamine-derived psychoactive alkaloid found mainly in the fungal genus Psilocybe, among others, and is the active ingredient in so-called "magic mushrooms". Although its notoriety originates from its psychotropic properties and popular use as a recreational drug, clinical trials have recently recognized psilocybin as a promising candidate for the treatment of various psychological and neurological afflictions. In this work, we demonstrate the de novo biosynthetic production of psilocybin and related tryptamine derivatives in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expression of a heterologous biosynthesis pathway sourced from Psilocybe cubensis. Additionally, we achieve improved product titers by supplementing the pathway with a novel cytochrome P450 reductase from P. cubensis. Further rational engineering resulted in a final production strain producing 627 ± 140 mg/L of psilocybin and 580 ± 276 mg/L of the dephosphorylated degradation product psilocin in triplicate controlled fed-batch fermentations in minimal synthetic media. Pathway intermediates baeocystin, nor norbaeocystin as well the dephosphorylated baeocystin degradation product norpsilocin were also detected in strains engineered for psilocybin production. We also demonstrate the biosynthetic production of natural tryptamine derivative aeruginascin as well as the production of a new-to-nature tryptamine derivative N-acetyl-4-hydroxytryptamine. These results lay the foundation for the biotechnological production of psilocybin in a controlled environment for pharmaceutical applications, and provide a starting point for the biosynthetic production of other tryptamine derivatives of therapeutic relevance.
Hell yeah. 1200 mg of alkaloids per liter means a 1 liter reactor could produce almost 250 5 milligram doses, or the equivalent of a gram of shrooms for every 8 mL of broth.
Move over, mushrooms!
Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of psilocybin and related tryptamine derivatives.
Milne N, Thomsen P, Knudsen NM, Rubaszka P, Kristensen M, Borodina I.
Psilocybin is a tryptamine-derived psychoactive alkaloid found mainly in the fungal genus Psilocybe, among others, and is the active ingredient in so-called "magic mushrooms". Although its notoriety originates from its psychotropic properties and popular use as a recreational drug, clinical trials have recently recognized psilocybin as a promising candidate for the treatment of various psychological and neurological afflictions. In this work, we demonstrate the de novo biosynthetic production of psilocybin and related tryptamine derivatives in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expression of a heterologous biosynthesis pathway sourced from Psilocybe cubensis. Additionally, we achieve improved product titers by supplementing the pathway with a novel cytochrome P450 reductase from P. cubensis. Further rational engineering resulted in a final production strain producing 627 ± 140 mg/L of psilocybin and 580 ± 276 mg/L of the dephosphorylated degradation product psilocin in triplicate controlled fed-batch fermentations in minimal synthetic media. Pathway intermediates baeocystin, nor norbaeocystin as well the dephosphorylated baeocystin degradation product norpsilocin were also detected in strains engineered for psilocybin production. We also demonstrate the biosynthetic production of natural tryptamine derivative aeruginascin as well as the production of a new-to-nature tryptamine derivative N-acetyl-4-hydroxytryptamine. These results lay the foundation for the biotechnological production of psilocybin in a controlled environment for pharmaceutical applications, and provide a starting point for the biosynthetic production of other tryptamine derivatives of therapeutic relevance.
Hell yeah. 1200 mg of alkaloids per liter means a 1 liter reactor could produce almost 250 5 milligram doses, or the equivalent of a gram of shrooms for every 8 mL of broth.
Move over, mushrooms!
sekio
Bluelight Crew
sulfate does not have that structure  that would imply the fully protonated form would be H4SO4.
that would imply the fully protonated form would be H4SO4.
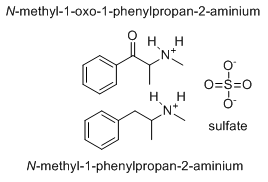
"Methyl-tom and methyl-jerry" ?

"Methyl-tom and methyl-jerry" ?
- Status
- Not open for further replies.



