dopamimetic
Bluelighter
This is an interesting part of the neurotransmitter puzzle.
"Through the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), the endocannabinoid system plays a physiological role in maintaining the activity of glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor within harmless limits. The influence of cannabinoids must be proportional to the stimulus in order to prevent NMDAR overactivation or exaggerated hypofunction that may precipitate symptoms of psychosis. In this framework, the recently reported association of CB1s with NMDARs, which mediates the reduction of cannabinoid analgesia promoted by NMDAR antagonism, could also support the precipitation of schizophrenia brought about by the abuse of smoked cannabis, mostly among vulnerable individuals. Accordingly, we have investigated this possibility using neuroprotection and analgesia as reporters of the CB1-NMDAR connection. We found that the Sigma 1 receptor (σ1R) acts as a safety switch, releasing NMDARs from the influence of CB1s and thereby avoiding glutamate hypofunction. In σ1R(-/-) mice the activity of NMDARs increases and cannot be regulated by cannabinoids, and NMDAR antagonism produces no effect on cannabinoid analgesia. In wild-type mice, ligands of the σ1R did not affect the CB1-NMDAR regulatory association, however, experimental NMDAR hypofunction enabled σ1R antagonists to release NMDARs from the negative control of CB1s. Of the σ1R antagonists tested, their order of activity was: S1RA > BD1047 ≫ NE100 = BD1063, although SKF10047, PRE-084 and (+)pentazocine were inactive yet able to abolish the effect of S1RA in this paradigm. Thus, the σ1R controls the extent of CB1-NMDAR interaction and its failure might constitute a vulnerability factor for cannabis abuse, potentially precipitating schizophrenia that might otherwise be induced later in time by the endogenous system."
 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
 www.nature.com
www.nature.com
Now, something is weird for me. I have increased NMDAr density, if not naturally then permatolerance from heavy disso use and symptoms which are consistent with glutamate overexcitation (I know it is poorly defined and coincidence is possible, yet it is an exact set of symptoms which all respond to NMDA antagonists, yet only partially to e.g. benzos). So THC should bring relief but it exacerbates things. Sigma-1 antagonists indeed have bad effects to me. But what puzzles me is that CBD helps, when it should actually increase NMDA currents and even that alone doesn't make sense as it should generally lead to increased and not decreased anxiety.
Here we have this:
"Biphasic effects of cannabinoids have been shown in processes such as feeding behavior, motor activity, motivational processes and anxiety responses. Using two different tests for the characterization of anxiety-related behavior (elevated plus-maze and holeboard), we first identified in wild-type C57BL/6N mice, two doses of the synthetic CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist CP-55,940 with anxiolytic (1 μg/kg) and anxiogenic properties (50 μg/kg), respectively. To clarify the role of CB1 receptors in this biphasic effect, both doses were applied to two different conditional CB1 receptor knockout (KO) mouse lines, GABA-CB1-KO (CB1 receptor inactivation in forebrain GABAergic neurons) and Glu-CB1-KO (CB1 receptor inactivation in cortical glutamatergic neurons). We found that the anxiolytic-like effects of the low dose of cannabinoids are mediated via the CB1 receptor on cortical glutamatergic terminals, because this anxiolytic-like response was abrogated only in Glu-CB1-KO mice. On the contrary, the CB1 receptor on the GABAergic terminals is required to induce an anxiogenic-like effect under a high-dose treatment because of the fact that this effect was abolished specifically in GABA-CB1-KO mice. These experiments were carried out in both sexes, and no differences occurred with the doses tested in the mutant mice. Interestingly, the positive allosteric modulation of GABA(B) receptor with GS-39783 was found to largely abrogate the anxiogenic-like effect of the high dose of CP-55,940. Our results shed new light in further understanding the biphasic effects of cannabinoids at the molecular level and, importantly, pave the way for the development of novel anxiolytic cannabinoid drugs, which may have favorable effect profiles targeting the CB1 receptor on glutamatergic terminals. "

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Then serotonin enters the game:
"Neuroanatomical findings revealed that CB1 cannabinoid and 5-HT3 receptors are coexpressed by a subtype of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneurons in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala, three brain regions that are crucial for the control of anxiety. In these regions, serotonergic inputs increase GABA release through 5-HT3 receptors, the phenomenon being retrogradely controlled by cannabinoid neurotransmission. This suggests a functional interaction between 5-HT3 neurotransmission and CB1 signaling. In a first attempt to investigate the behavioral relevance of these interactions, we studied the effects of the selective 5-HT3 agonist 1-(m-chlorophenyl)-biguanide (mCPBG), on plus-maze behavior in NMRI, CD1 wild type, and CB1-KO mice. The genetic disruption of CB1 receptors consistently increased anxiety. This effect was significantly decreased by the 5-HT3 agonist, mCPBG. The dose-response curve was bell-shaped. Surprisingly, mCPBG did not affect the behavior of CD1 wild type and NMRI mice. We hypothesize that in the aforementioned regions, 5-HT3 activation decreases anxiety by promoting GABA release, but this effect is dampened by CB1 signaling. The disruption of CB1 receptors in CB1-KOs released GABA neurons from retrograde inhibition and made the effects of 5-HT3 stimulation conspicuous. Altogether, our findings reveal a functional interaction between 5-HT3 neurotransmission and CB1 signaling. Besides this interaction being an interesting aspect of anxiety control, it may also explain the notoriously inconsistent effects of 5-HT3 ligands on anxiety. If 5-HT3 neurotransmission and CB1 signaling interact, the anxiety-related effects of 5-HT3 ligands may depend on species, strain, and situation-related differences in both 5-HT3 and CB1 receptor expression and function. "

 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Guess I am oversimplificating but the topic is interesting.
"Through the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), the endocannabinoid system plays a physiological role in maintaining the activity of glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor within harmless limits. The influence of cannabinoids must be proportional to the stimulus in order to prevent NMDAR overactivation or exaggerated hypofunction that may precipitate symptoms of psychosis. In this framework, the recently reported association of CB1s with NMDARs, which mediates the reduction of cannabinoid analgesia promoted by NMDAR antagonism, could also support the precipitation of schizophrenia brought about by the abuse of smoked cannabis, mostly among vulnerable individuals. Accordingly, we have investigated this possibility using neuroprotection and analgesia as reporters of the CB1-NMDAR connection. We found that the Sigma 1 receptor (σ1R) acts as a safety switch, releasing NMDARs from the influence of CB1s and thereby avoiding glutamate hypofunction. In σ1R(-/-) mice the activity of NMDARs increases and cannot be regulated by cannabinoids, and NMDAR antagonism produces no effect on cannabinoid analgesia. In wild-type mice, ligands of the σ1R did not affect the CB1-NMDAR regulatory association, however, experimental NMDAR hypofunction enabled σ1R antagonists to release NMDARs from the negative control of CB1s. Of the σ1R antagonists tested, their order of activity was: S1RA > BD1047 ≫ NE100 = BD1063, although SKF10047, PRE-084 and (+)pentazocine were inactive yet able to abolish the effect of S1RA in this paradigm. Thus, the σ1R controls the extent of CB1-NMDAR interaction and its failure might constitute a vulnerability factor for cannabis abuse, potentially precipitating schizophrenia that might otherwise be induced later in time by the endogenous system."
The cannabinoid receptor 1 associates with NMDA receptors to produce glutamatergic hypofunction: implications in psychosis and schizophrenia - PMC
The endocannabinoid system is widespread throughout the central nervous system and its type 1 receptor (CB1) plays a crucial role in preventing the neurotoxicity caused by activation of glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). Indeed, it ...

The calcium-sensitive Sigma-1 receptor prevents cannabinoids from provoking glutamate NMDA receptor hypofunction: implications in antinociception and psychotic diseases - PubMed
Through the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), the endocannabinoid system plays a physiological role in maintaining the activity of glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor within harmless limits. The influence of cannabinoids must be proportional to the stimulus in order to prevent NMDAR...

Cannabinoid receptors couple to NMDA receptors to reduce the production of NO and the mobilization of zinc induced by glutamate - PubMed
Cannabinoids require the HINT1 protein to counteract the toxic effects of NMDAR-mediated NO production and zinc release. This study situates the HINT1 protein at the forefront of cannabinoid protection against NMDAR-mediated brain damage.

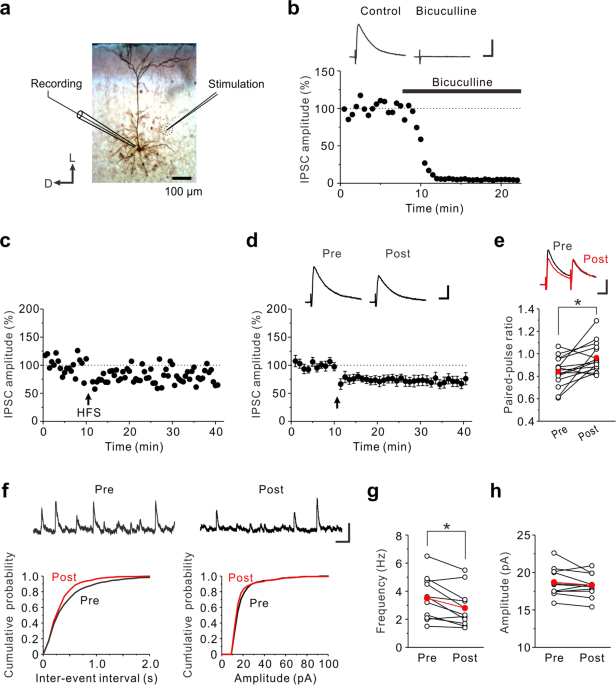
CB1 cannabinoid receptor-mediated plasticity of GABAergic synapses in the mouse insular cortex - Scientific Reports
The insular cortex plays pivotal roles in taste learning. As cellular mechanisms of taste learning, long-term potentiation (LTP) at glutamatergic synapses is well studied. However, little is known about long-term changes of synaptic efficacy at GABAergic synapses in the insular cortex. Here, we...
Now, something is weird for me. I have increased NMDAr density, if not naturally then permatolerance from heavy disso use and symptoms which are consistent with glutamate overexcitation (I know it is poorly defined and coincidence is possible, yet it is an exact set of symptoms which all respond to NMDA antagonists, yet only partially to e.g. benzos). So THC should bring relief but it exacerbates things. Sigma-1 antagonists indeed have bad effects to me. But what puzzles me is that CBD helps, when it should actually increase NMDA currents and even that alone doesn't make sense as it should generally lead to increased and not decreased anxiety.
Here we have this:
"Biphasic effects of cannabinoids have been shown in processes such as feeding behavior, motor activity, motivational processes and anxiety responses. Using two different tests for the characterization of anxiety-related behavior (elevated plus-maze and holeboard), we first identified in wild-type C57BL/6N mice, two doses of the synthetic CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist CP-55,940 with anxiolytic (1 μg/kg) and anxiogenic properties (50 μg/kg), respectively. To clarify the role of CB1 receptors in this biphasic effect, both doses were applied to two different conditional CB1 receptor knockout (KO) mouse lines, GABA-CB1-KO (CB1 receptor inactivation in forebrain GABAergic neurons) and Glu-CB1-KO (CB1 receptor inactivation in cortical glutamatergic neurons). We found that the anxiolytic-like effects of the low dose of cannabinoids are mediated via the CB1 receptor on cortical glutamatergic terminals, because this anxiolytic-like response was abrogated only in Glu-CB1-KO mice. On the contrary, the CB1 receptor on the GABAergic terminals is required to induce an anxiogenic-like effect under a high-dose treatment because of the fact that this effect was abolished specifically in GABA-CB1-KO mice. These experiments were carried out in both sexes, and no differences occurred with the doses tested in the mutant mice. Interestingly, the positive allosteric modulation of GABA(B) receptor with GS-39783 was found to largely abrogate the anxiogenic-like effect of the high dose of CP-55,940. Our results shed new light in further understanding the biphasic effects of cannabinoids at the molecular level and, importantly, pave the way for the development of novel anxiolytic cannabinoid drugs, which may have favorable effect profiles targeting the CB1 receptor on glutamatergic terminals. "

Biphasic effects of cannabinoids in anxiety responses: CB1 and GABA(B) receptors in the balance of GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission - PubMed
Biphasic effects of cannabinoids have been shown in processes such as feeding behavior, motor activity, motivational processes and anxiety responses. Using two different tests for the characterization of anxiety-related behavior (elevated plus-maze and holeboard), we first identified in...
Then serotonin enters the game:
"Neuroanatomical findings revealed that CB1 cannabinoid and 5-HT3 receptors are coexpressed by a subtype of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneurons in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala, three brain regions that are crucial for the control of anxiety. In these regions, serotonergic inputs increase GABA release through 5-HT3 receptors, the phenomenon being retrogradely controlled by cannabinoid neurotransmission. This suggests a functional interaction between 5-HT3 neurotransmission and CB1 signaling. In a first attempt to investigate the behavioral relevance of these interactions, we studied the effects of the selective 5-HT3 agonist 1-(m-chlorophenyl)-biguanide (mCPBG), on plus-maze behavior in NMRI, CD1 wild type, and CB1-KO mice. The genetic disruption of CB1 receptors consistently increased anxiety. This effect was significantly decreased by the 5-HT3 agonist, mCPBG. The dose-response curve was bell-shaped. Surprisingly, mCPBG did not affect the behavior of CD1 wild type and NMRI mice. We hypothesize that in the aforementioned regions, 5-HT3 activation decreases anxiety by promoting GABA release, but this effect is dampened by CB1 signaling. The disruption of CB1 receptors in CB1-KOs released GABA neurons from retrograde inhibition and made the effects of 5-HT3 stimulation conspicuous. Altogether, our findings reveal a functional interaction between 5-HT3 neurotransmission and CB1 signaling. Besides this interaction being an interesting aspect of anxiety control, it may also explain the notoriously inconsistent effects of 5-HT3 ligands on anxiety. If 5-HT3 neurotransmission and CB1 signaling interact, the anxiety-related effects of 5-HT3 ligands may depend on species, strain, and situation-related differences in both 5-HT3 and CB1 receptor expression and function. "

Interactions between the anxiogenic effects of CB1 gene disruption and 5-HT3 neurotransmission - PubMed
Neuroanatomical findings revealed that CB1 cannabinoid and 5-HT3 receptors are coexpressed by a subtype of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneurons in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala, three brain regions that are crucial for the control of anxiety. In these...
Guess I am oversimplificating but the topic is interesting.



