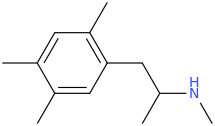
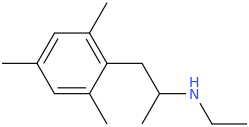
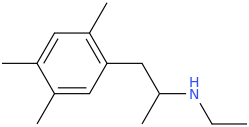
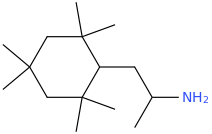
-
Neuroscience & Pharmacology Discussion Welcome Guest
Posting Rules Bluelight Rules Recent Journal Articles Chemistry Mega-Thread FREE Chemistry Databases! Self-Education Guide -
N&PD Moderators: Skorpio | someguyontheinternet
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
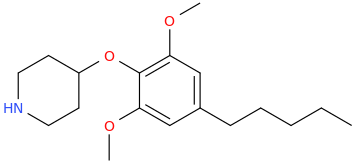
Ketamine salts solubility
- Thread starter fastandbulbous
- Start date
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
Synergistic interaction between the agonism of cebranopadol at nociceptin/orphanin FQ and classical opioid receptors in the rat spinal nerve ligation model
Corresponding author: Thomas Christoph (Preclinical Drug Development, Grunenthal GmbH, Aachen, Germany)
Pharmacology Research & Perspectives 2018, Volume 6, Issue 6, Page e00444
Published online November 28th, 2018
https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.444
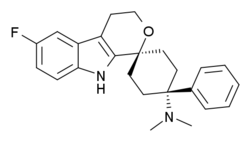
Could Grunenthal be in the lead in the race towards a "less abusable" painkiller? I wonder how the trials are going for this one.
EDIT: the main Phase 3 trial was terminated while a smaller open-label extension of that trial was completed in 2016. That doesn't seem to bode well, but the FDA has a lot of pressure right now to approve any kind of alternative painkiller, so who knows.
Corresponding author: Thomas Christoph (Preclinical Drug Development, Grunenthal GmbH, Aachen, Germany)
Pharmacology Research & Perspectives 2018, Volume 6, Issue 6, Page e00444
Published online November 28th, 2018
https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.444
Cebranopadol:Cebranopadol (trans‐6'‐fluoro‐4',9'‐dihydro‐N,N‐dimethyl‐4‐phenyl‐spiro[cyclohexane‐1,1'(3'H)‐pyrano[3,4‐b]indol]‐4‐amine) is a novel analgesic nociceptin/orphanin FQ opioid peptide (NOP) and classical opioid receptor (MOP, DOP, and KOP) agonist with highly efficacious and potent activity in a broad range of rodent models of nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic pain as well as limited opioid‐type side effects such as respiratory depression. This study was designed to explore contribution and interaction of NOP and classical opioid receptor agonist components to cebranopadol analgesia in the rat spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model. Assessing antihypersensitive activity in SNL rats intraperitoneal (IP) administration of cebranopadol resulted in ED50 values of 3.3 and 3.58 μg/kg in two independent experiments. Pretreatment (IP) with J‐113397 (4.64 mg/kg) a selective antagonist for the NOP receptor or naloxone (1 mg/kg), naltrindole (10 mg/kg), or nor‐BNI (10 mg/kg), selective antagonists for MOP, DOP, and KOP receptors, yielded ED50 values of 14.1, 16.9, 17.3, and 15 μg/kg, respectively. This 4‐5 fold rightward shift of the dose‐response curves suggested agonistic contribution of all four receptors to the analgesic activity of cebranopadol. Combined pretreatment with a mixture of the antagonists for the three classical opioid receptors resulted in an 18‐fold potency shift with an ED50 of 65.5 μg/kg. The concept of dose equivalence was used to calculate the expected additive effects of the parent compound for NOP and opioid receptor contribution and to compare them with the observed effects, respectively. This analysis revealed a statistically significant difference between the expected additive and the observed effects suggesting intrinsic synergistic analgesic interaction of the NOP and the classical opioid receptor components of cebranopadol. Together with the observation of limited respiratory depression in rats and humans the synergistic interaction of NOP and classical opioid receptor components in analgesia described in the current study may contribute to the favorable therapeutic index of cebranopadol observed in clinical trials.

Could Grunenthal be in the lead in the race towards a "less abusable" painkiller? I wonder how the trials are going for this one.
EDIT: the main Phase 3 trial was terminated while a smaller open-label extension of that trial was completed in 2016. That doesn't seem to bode well, but the FDA has a lot of pressure right now to approve any kind of alternative painkiller, so who knows.
Last edited:
I'm surprised that 2-Br LSD (or LSD analogue) isn't an item of commerce. No activity whatsoever and a gentle reduction yields active in 78% yield (I guess you just leave it in there). It isn't an API but it means people can make the immediate precursor on a large scale for people to finish.
https://imgur.com/a/H3QZvQf
I just thought I would post a 'novel' opioid based on several Janssen patents. It turns out a carbamate ester is a bioisostere of an amide in this case (goodbye MoDA), that 3,3-disubstitution is fine and unless you are going to resolve the enantiomers, is more potent than 3-MF and if you DO resolve, it's only the lower MW of 3-MF that makes it marginally stronger. The thiazole proves to be as potent as the 2-furyl (i.e. twice as potent as the 2-thienyl) and unexpectedly has a duration some x4 longer. I can only presume that the liver enzyme(s) responsible for N-dealkylation have trouble with that aromatic (oxazoles also work but the LogP isn't as favourable). The o-F is just my little joke, 2-fluoroaniline just means 1 more thing to watch but it isn't like more resources appear to actually DO so.
In short, while NPP (N-phenylethyl-4-piperidone) is still the precursor-of-choice (and is watched), 3,3-dimethyl-1-[2-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)ethyl]piperidin-4-one is an item of commerce. Good luck with the ethyl chloroformate!
It's purely given as an example of just how easy it is to avoid the MoDA and 'watched' precursors. That people aren't even bothering kind of hints that control isn't working AT ALL. That does anger me since fentanyl has become a disaster area with 1000s of people ending up dead from C cut with F. I suspect the authorities aren't really trying very hard.
-----
https://imgur.com/a/JYeLkLt
Mate in 3. I checked with the Home Office and as long as the precursor is intended as a precursor, not as a medicine, I don't even need a licence. OK, it's 3 steps (as opposed to 2 for fentanyl) but that 14-methoxy appears to produce a LOT of delta activity even in the absence of the ether bridge. I'm just pointing out that some REALLY potent stuff is within anyone's reach. The MoDA doesn't cover it! I'm not defending people making this stuff, I'm just appraising people of the fact that it's not exactly difficult to make the stuff and where there is ? to be made, people will.
I admit that the alkylation of the tertiary alcohol is a bit of a pain. Schmidhammer does at least go for an 'uneventful' route but it's and interesting problem. In this case, the absence of certain moieties does make the scaffold more robust (that bridge is a sod for breaking).
-----
https://imgur.com/a/SKCnQFC
One for the training set. It overlays BDPC spectacularly well although Dr. Lednicer had never come across it. So will a m-OH or p-Br work? I'm going to say YES. Will replacing the acetophenone moiety with a different aromatic work. I'm going to say yes. Dimethylaminopivalophenone follows the classic mu training set but like BDPC, this compound shows that you can move that basic nitrogen. I vaguely remember another scaffold with a secondary amine that overlaid BDPC but it had to much sigma affinity. Still, it's all good for your training sets.
I just thought I would post a 'novel' opioid based on several Janssen patents. It turns out a carbamate ester is a bioisostere of an amide in this case (goodbye MoDA), that 3,3-disubstitution is fine and unless you are going to resolve the enantiomers, is more potent than 3-MF and if you DO resolve, it's only the lower MW of 3-MF that makes it marginally stronger. The thiazole proves to be as potent as the 2-furyl (i.e. twice as potent as the 2-thienyl) and unexpectedly has a duration some x4 longer. I can only presume that the liver enzyme(s) responsible for N-dealkylation have trouble with that aromatic (oxazoles also work but the LogP isn't as favourable). The o-F is just my little joke, 2-fluoroaniline just means 1 more thing to watch but it isn't like more resources appear to actually DO so.
In short, while NPP (N-phenylethyl-4-piperidone) is still the precursor-of-choice (and is watched), 3,3-dimethyl-1-[2-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)ethyl]piperidin-4-one is an item of commerce. Good luck with the ethyl chloroformate!
It's purely given as an example of just how easy it is to avoid the MoDA and 'watched' precursors. That people aren't even bothering kind of hints that control isn't working AT ALL. That does anger me since fentanyl has become a disaster area with 1000s of people ending up dead from C cut with F. I suspect the authorities aren't really trying very hard.
-----
https://imgur.com/a/JYeLkLt
Mate in 3. I checked with the Home Office and as long as the precursor is intended as a precursor, not as a medicine, I don't even need a licence. OK, it's 3 steps (as opposed to 2 for fentanyl) but that 14-methoxy appears to produce a LOT of delta activity even in the absence of the ether bridge. I'm just pointing out that some REALLY potent stuff is within anyone's reach. The MoDA doesn't cover it! I'm not defending people making this stuff, I'm just appraising people of the fact that it's not exactly difficult to make the stuff and where there is ? to be made, people will.
I admit that the alkylation of the tertiary alcohol is a bit of a pain. Schmidhammer does at least go for an 'uneventful' route but it's and interesting problem. In this case, the absence of certain moieties does make the scaffold more robust (that bridge is a sod for breaking).
-----
https://imgur.com/a/SKCnQFC
One for the training set. It overlays BDPC spectacularly well although Dr. Lednicer had never come across it. So will a m-OH or p-Br work? I'm going to say YES. Will replacing the acetophenone moiety with a different aromatic work. I'm going to say yes. Dimethylaminopivalophenone follows the classic mu training set but like BDPC, this compound shows that you can move that basic nitrogen. I vaguely remember another scaffold with a secondary amine that overlaid BDPC but it had to much sigma affinity. Still, it's all good for your training sets.
Last edited:
https://imgur.com/a/JYeLkLt
Mate in 3. I checked with the Home Office and as long as the precursor is intended as a precursor, not as a medicine, I don't even need a licence. OK, it's 3 steps (as opposed to 2 for fentanyl) but that 14-methoxy appears to produce a LOT of delta activity even in the absence of the ether bridge.
It's nice that the MoDA doesn't have a blanket ban on morphinans. That said, I'm not sure what uncontrolled commodity chemical would serve as a viable precursor to the compound drawn. I'm curious what you had in mind.
It's nice that the MoDA doesn't have a blanket ban on morphinans. That said, I'm not sure what uncontrolled commodity chemical would serve as a viable precursor to the compound drawn. I'm curious what you had in mind.
Well 1-[2-(furan-2-yl)ethyl]-3,3-dimethylpiperidin-4-one is certainly available. Anyone who knows the Mole people will know exactly where to get it from. I am still amazed at the amount of 2-nitroprop-1-en-1-ylbenzene they still sell. An RT reaction between benzaldehyde & nitroethane with NaOH catalyst is a stroke of genius. Who cares if someone can do it in 2 hours. If the chemist can just fill the reactor at the end of the day, the product is ready for the next day. They have gone a bit off-radar and so I'm guessing they have all the customers they need (how much does a Kg of the nitropropene cost to make?).
The mad major sells just about every ring-substituted aldehyde, nitrostyrene, nitropropene and aryl-methyl ketone known to man. His attempt to distil 3,5-diamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzaldehyde still makes me laugh. That is his thing. They carefully consulted the MoDA and just ensured that, along with the Poisons Act & the Explosive acts, they weren't breaking the law.
They set me a puzzle that I'm still unable to solve. It's a 1-step route to PMK using only 1 organic compound & 2 inorganic compounds and almost 100% conversion takes place promptly at 64?C (the smell is their right on the button so it happens fast). I think it's a Russian or Chinese paper but I don't think ANYONE ever solved that one.
https://imgur.com/a/L6ZmCBP
Pyeyzolam (known to the Eunoiapharmacopia crew) as explained by OrangeJuice
The Patent Application:
(Journal 6751), GB1813962.6, Applicant: Alcarelle Holdings Limited Title: Mood enhancing compounds. Date Lodged: 28 August 2018
IS this compound. Sadly it only mimics drunk, not a couple of glasses of wine. No problem, my own patents (synth by Ukranian Team) DOES fully replace ethanol.
Would you believe that all of the subjective negative effects of alcohol are mediated by the GABA a1b2d2 subtype and all of the positive effects of alcohol are mediated by the a5b2d2? All of you who tried the 3mf tablets will know that a couple do almost nothing, 8 makes you feel like you imbibed a 1/2 bottle of vodka instantly. So it isn't perfect. Happily I now have a very long-acting ligand (to treat the alcohol dependant) and a thienobenzo that mimics ethanol really well.
I would just like to thank all of the Eunoiapharmacopia crew. Would you believe that isophenidine didn't happen because the shitty chemists removed the H2O thermally so an amine with a low MW wasn't possible. That a RT, fast, cheap route was known was thrown out because they couldn't charge much (given how cheap it was). Truly, in the RC era, people still looked for max profit and diphenidine should never have been distributed. I feel bad about that. I do hope people enjoyed the pynazolam - that was our (me and my family) favourite. We LOVED it.
That the aminorex didn't appear was limited chemistry ability as well.....
Pyeyzolam (known to the Eunoiapharmacopia crew) as explained by OrangeJuice
The Patent Application:
(Journal 6751), GB1813962.6, Applicant: Alcarelle Holdings Limited Title: Mood enhancing compounds. Date Lodged: 28 August 2018
IS this compound. Sadly it only mimics drunk, not a couple of glasses of wine. No problem, my own patents (synth by Ukranian Team) DOES fully replace ethanol.
Would you believe that all of the subjective negative effects of alcohol are mediated by the GABA a1b2d2 subtype and all of the positive effects of alcohol are mediated by the a5b2d2? All of you who tried the 3mf tablets will know that a couple do almost nothing, 8 makes you feel like you imbibed a 1/2 bottle of vodka instantly. So it isn't perfect. Happily I now have a very long-acting ligand (to treat the alcohol dependant) and a thienobenzo that mimics ethanol really well.
I would just like to thank all of the Eunoiapharmacopia crew. Would you believe that isophenidine didn't happen because the shitty chemists removed the H2O thermally so an amine with a low MW wasn't possible. That a RT, fast, cheap route was known was thrown out because they couldn't charge much (given how cheap it was). Truly, in the RC era, people still looked for max profit and diphenidine should never have been distributed. I feel bad about that. I do hope people enjoyed the pynazolam - that was our (me and my family) favourite. We LOVED it.
That the aminorex didn't appear was limited chemistry ability as well.....

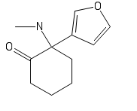
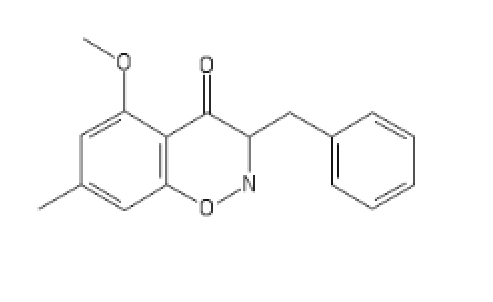
I'll call this new cumpound the D (COC bond and a Ketone; get it?)
The new DCK every disso addict will be boofing. haha (please Don't ban me)
And a little inspiration; I recommand Bird Box (movie about mass psychosis due to entities) and Annihilation, basically TDS stuff but in a movie.
The new DCK every disso addict will be boofing. haha (please Don't ban me)
And a little inspiration; I recommand Bird Box (movie about mass psychosis due to entities) and Annihilation, basically TDS stuff but in a movie.
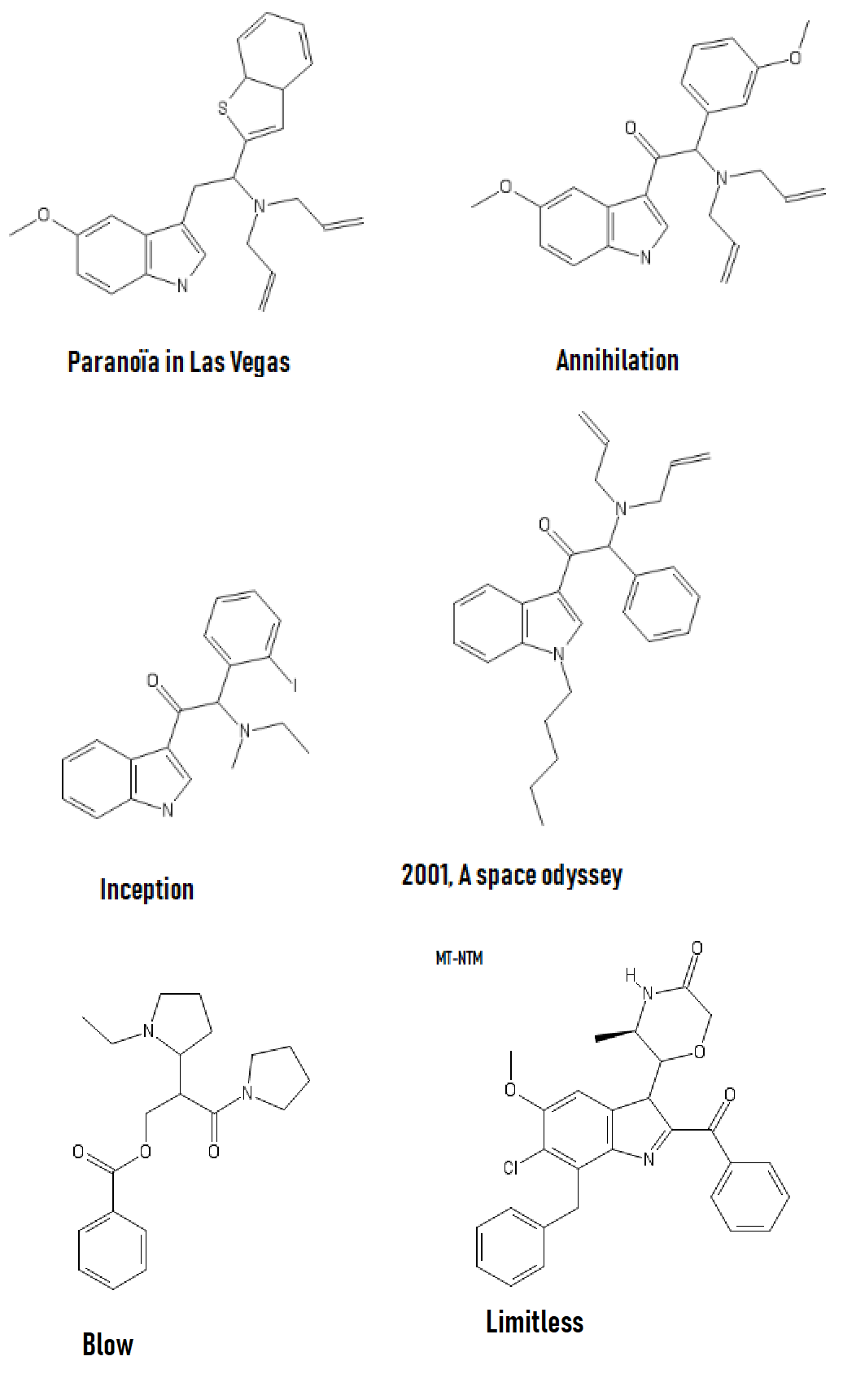
Could someone come up with a NMDA agonist other than those proposed by wiki? Interested by how it lay interact with the consciousness of oneself and its environment.
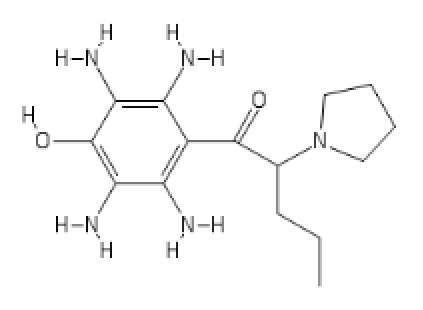
presumed Deadly toxic, I proudly present
U-47007 (tapent-(tapant = hitting in french (hitman hint))-adol :
presumed Deadly toxic, I proudly present
U-47007 (tapent-(tapant = hitting in french (hitman hint))-adol :
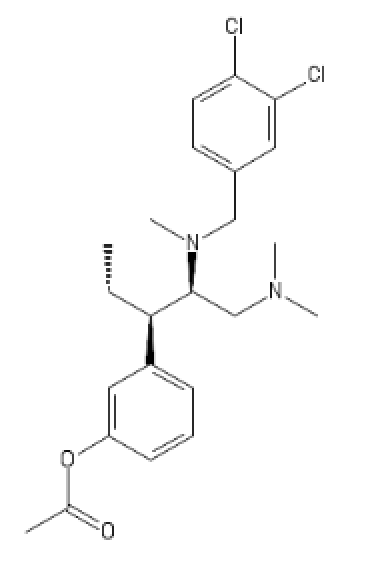
(probably has some HT activity)
Last edited:
5-HT2 receptor binding, functional activity and selectivity in N-benzyltryptamines
Corresponding author: Bruce K. Cassels (Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University of Chile, Nunoa, Chile)
PLOS One 2019, Volume 14, Issue 1, Page e0209804
Published online January 10th, 2019
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209804
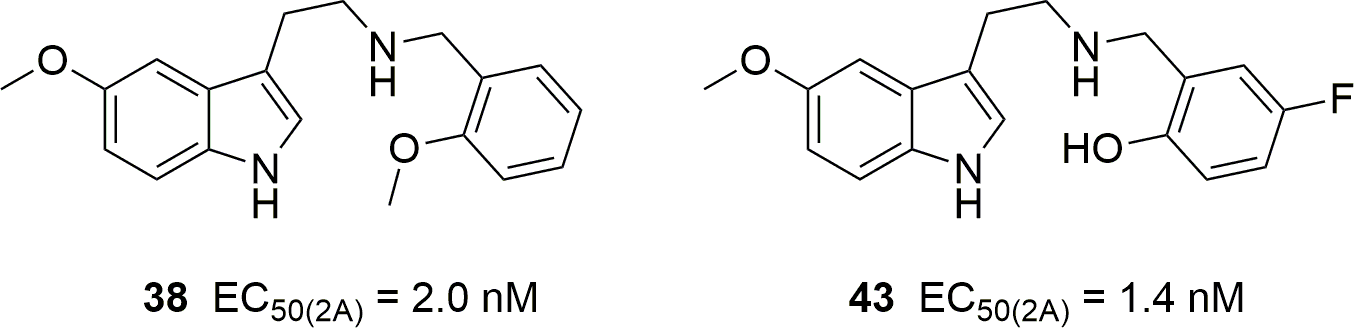
Corresponding author: Bruce K. Cassels (Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University of Chile, Nunoa, Chile)
PLOS One 2019, Volume 14, Issue 1, Page e0209804
Published online January 10th, 2019
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209804
The authors suggest that the following two compounds "might be human hallucinogens in the low milligram dose range." The compound on the left had already been studied by Nichols.The last fifteen years have seen the emergence and overflow into the drug scene of "superpotent" N-benzylated phenethylamines belonging to the "NBOMe" series, accompanied by numerous research articles. Although N-benzyl substitution of 5-methoxytryptamine is known to increase its affinity and potency at 5-HT2 receptors associated with psychedelic activity, N-benzylated tryptamines have been studied much less than their phenethylamine analogs. To further our knowledge of the activity of N-benzyltryptamines, we have synthesized a family of tryptamine derivatives and, for comparison, a few 5-methoxytryptamine analogs with many different substitution patterns on the benzyl moiety, and subjected them to in vitro affinity and functional activity assays vs. the human 5-HT2 receptor subtypes. In the binding (radioligand displacement) studies some of these compounds exhibited only modest selectivity for either 5-HT2A or 5-HT2C receptors suggesting that a few of them, with affinities in the 10–100 nanomolar range for 5-HT2A receptors, might presumably be psychedelic. Unexpectedly, their functional (calcium mobilization) assays reflected very different trends. All of these compounds proved to be 5-HT2C receptor full agonists while most of them showed low efficacy at the 5-HT2A subtype. Furthermore, several showed moderate-to-strong preferences for activation of the 5-HT2C subtype at nanomolar concentrations. Thus, although some N-benzyltryptamines might be abuse-liable, others might represent new leads for the development of therapeutics for weight loss, erectile dysfunction, drug abuse, or schizophrenia.
Last edited:
I'm sure people will have discovered the papers covering the exhaustive studies on the 1-aryl-cyclohexylamine class off NMDA antagonist/DRI class (Erowid has a vault on all of that stuff) so when UK law made the scaffold illegal, the only novel alternative looked at back in the 60s was a single small study on 1-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperidine so that was the intended lead-compound to explore the class. So, the custom-synth people weren't fantastic and they sent 1-(1,2-diphenylethyl)pyrrolidine! Idiots. Well, there is a very important relationship between the position of 1-aryl & the lone-pair of the N: (107.5 is the best as seen in Dizocilpine) so we KNEW it wouldn't have NMDA activity but wanted to confirm that it had DRI activity (NMDA antagonism without DRI activity is generally not so euphoric). Well, only a slight surprise to discover that it was subjectively identical (as far as we could tell) to prolintane. A very smooth, very selective DRI). So as soon as they DID manage to provide the specified ligand, it was immediately put through the Eunoiapharmacopia crew (hello from OranheJuice) who... ate it, because the .HCl wasn't too water soluble! Anyway, apart from discovering that isophenidine is THE one to go for (MXE nice), it's not such an interesting find... but the fact that a second benzene ring acts as a bioisostere to an N-propyl certainly WAS. So we went this way:
1-(1,2-diphenylethyl)pyrrolidine - not TOO potent, really smooth. I liked it a lot but I was told young people wanted something more so
1,2-diphenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - a LOT more like pyrovalerone but had that tendency to hang on for too long. Fun for 2 hours then, like cocaine (which I don't really care for truth be told), it just hangs on. So...
1-(4-methylphenyl)-2-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - The p-Me didn't increase potency but it meant that the subjective effects tailed off much more quickly beyond the 2 hour mark and that was pyrophenidone (which I know people liked)
but we DID go further
1-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)-2-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - the indene ring was added to check if it were possible to improve serotonin reuptake inhibition. Was is us or did that p-Me FEEL a bit better? If so was it S related. No.
1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - So obviously we wanted to know if like MDPV, the MD ring would increase DRI activity. It did but it was costly and not as smooth. The p-Me was nicer.
Meanwhile we obviously tried various other N substituents (and found the QSAR was more like PCP than K). The 2-F was tasted (not by me) but the EC crew all wanted that. Turned out that the ketone->amine step via NaBH4 stripped off that -F (or indeed the -Cl) which is why 2-MeO turned up. The N-methyl & N-ethyl didn't have much activity but a series was made with various substituents at the o,m & p position (the 2-Cl 5-MeO was good, the 2-Cl-5-OH was great... but too costly).
It was interesting to know that an MD can seemingly increase VMAT-2 affinity and that it isn't strictly serotonin. I know people placed MD rings onto several rigid PEA derivatives including the phenmetrazine, phenylmethylpiperidine esters (methylphenidate/levophacetoperane) & aminorex scaffolds. It isn't rewarding. The only commonality across them all is the monosubstitution of the m or p positions. As I have posted elsewhere, a 2:1 mixture of p-Me aminorex:m-Me aminorex is like MDMA on steroids. The p is a serotonin releaser, the m is mixed but mostly a dopamine releaser. Now, existing as a zwitterion as the 4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine ring does, BOTH isomers are active since the exo form overlays MDA while the endo form overlays MDA. We worked that out afterwards. All we knew was that the p alone was inactive in most people, the m alone was just a stimulant & the 1:1 was too speedy. The 2:1 has the body rushes & legs of MDA (that 'sledging' & hugging yourself stuff) AND the euphoria and entactogenic effects of MDMA.
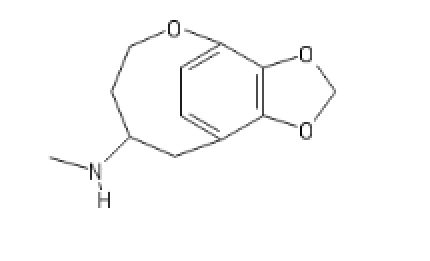
Since those long gone days I've spotted that 5/6(M)APB is taken from a patent (that Dr. Zee guy is a liar) and wondered about related rings. I cannot recall if it was Dr. Dave or Dr. Shulgin who tried adding an -F or two onto the methylene bridge (resulting in much lower potency) but I've not come across any studies using a benzoxathiol-6-yl or related (3H-2,1-benzoxathiolyl, 1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran, 1,3-dihydro-benzothio and so on) ring. I SUSPECT that the aromatic has to be rotatable relative to the basic amine(s) for any ring supplying a lone-pair to work and I suspect that planer (so unsaturated) increases potency and shortens at least one bond-length so there is a little more space (if the -F derivatives were less potent due to lower affinity itself due to physical size. I mean, we know PMA & PMMA are pretty dangerous and people making 'ecstacy' using them is basically guilty of intentionally poisoning people (even the 2-carbon 5HT2a ligands seem toxic) BUT I would (very cautiously) taste the benzothiophene homologues of APB. 4MTA (p-thiomethoxy) is a more potent serotonin releaser that 4MA (p-methoxy), it's the MAOI activity that seems to make it more dangerous.
Most of these I've tasted, some I've had multiple reports on, at least 2 I WISH were available (p/m aminorex & isophenidine) and there are some that look like they are worth a liik (benzothiophene) but I think if I can compress it all down to a single point. An MD ring isn't magical. You can't just add it to any stimulant with a phenyl ring and 'E it up'. I know that thiopropamine was 'rediscovered' by someone on Russian Hyperlab so I checked & the 3,4 & 5 carbon cathinone have been made and in rat models at least, 1-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pentan-1-one was the most potent. I'm prepared to bet ?1 that 1-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propan-1-one will prove to be mephedrone-like and MAYBE 2-(methylamino)-1-(thieno[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)propan-1-one & N-methyl-1-(thieno[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)propan-2-amine will turn out to be like inferior versions of methylone & MDMA. As we proved with the 2-carbon ketone analogues of 2CB still have 5HT2a activity. That last one was a French idea...
1-(1,2-diphenylethyl)pyrrolidine - not TOO potent, really smooth. I liked it a lot but I was told young people wanted something more so
1,2-diphenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - a LOT more like pyrovalerone but had that tendency to hang on for too long. Fun for 2 hours then, like cocaine (which I don't really care for truth be told), it just hangs on. So...
1-(4-methylphenyl)-2-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - The p-Me didn't increase potency but it meant that the subjective effects tailed off much more quickly beyond the 2 hour mark and that was pyrophenidone (which I know people liked)
but we DID go further
1-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)-2-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - the indene ring was added to check if it were possible to improve serotonin reuptake inhibition. Was is us or did that p-Me FEEL a bit better? If so was it S related. No.
1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethanone - So obviously we wanted to know if like MDPV, the MD ring would increase DRI activity. It did but it was costly and not as smooth. The p-Me was nicer.
Meanwhile we obviously tried various other N substituents (and found the QSAR was more like PCP than K). The 2-F was tasted (not by me) but the EC crew all wanted that. Turned out that the ketone->amine step via NaBH4 stripped off that -F (or indeed the -Cl) which is why 2-MeO turned up. The N-methyl & N-ethyl didn't have much activity but a series was made with various substituents at the o,m & p position (the 2-Cl 5-MeO was good, the 2-Cl-5-OH was great... but too costly).
It was interesting to know that an MD can seemingly increase VMAT-2 affinity and that it isn't strictly serotonin. I know people placed MD rings onto several rigid PEA derivatives including the phenmetrazine, phenylmethylpiperidine esters (methylphenidate/levophacetoperane) & aminorex scaffolds. It isn't rewarding. The only commonality across them all is the monosubstitution of the m or p positions. As I have posted elsewhere, a 2:1 mixture of p-Me aminorex:m-Me aminorex is like MDMA on steroids. The p is a serotonin releaser, the m is mixed but mostly a dopamine releaser. Now, existing as a zwitterion as the 4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine ring does, BOTH isomers are active since the exo form overlays MDA while the endo form overlays MDA. We worked that out afterwards. All we knew was that the p alone was inactive in most people, the m alone was just a stimulant & the 1:1 was too speedy. The 2:1 has the body rushes & legs of MDA (that 'sledging' & hugging yourself stuff) AND the euphoria and entactogenic effects of MDMA.
Since those long gone days I've spotted that 5/6(M)APB is taken from a patent (that Dr. Zee guy is a liar) and wondered about related rings. I cannot recall if it was Dr. Dave or Dr. Shulgin who tried adding an -F or two onto the methylene bridge (resulting in much lower potency) but I've not come across any studies using a benzoxathiol-6-yl or related (3H-2,1-benzoxathiolyl, 1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran, 1,3-dihydro-benzothio and so on) ring. I SUSPECT that the aromatic has to be rotatable relative to the basic amine(s) for any ring supplying a lone-pair to work and I suspect that planer (so unsaturated) increases potency and shortens at least one bond-length so there is a little more space (if the -F derivatives were less potent due to lower affinity itself due to physical size. I mean, we know PMA & PMMA are pretty dangerous and people making 'ecstacy' using them is basically guilty of intentionally poisoning people (even the 2-carbon 5HT2a ligands seem toxic) BUT I would (very cautiously) taste the benzothiophene homologues of APB. 4MTA (p-thiomethoxy) is a more potent serotonin releaser that 4MA (p-methoxy), it's the MAOI activity that seems to make it more dangerous.
Most of these I've tasted, some I've had multiple reports on, at least 2 I WISH were available (p/m aminorex & isophenidine) and there are some that look like they are worth a liik (benzothiophene) but I think if I can compress it all down to a single point. An MD ring isn't magical. You can't just add it to any stimulant with a phenyl ring and 'E it up'. I know that thiopropamine was 'rediscovered' by someone on Russian Hyperlab so I checked & the 3,4 & 5 carbon cathinone have been made and in rat models at least, 1-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pentan-1-one was the most potent. I'm prepared to bet ?1 that 1-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propan-1-one will prove to be mephedrone-like and MAYBE 2-(methylamino)-1-(thieno[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)propan-1-one & N-methyl-1-(thieno[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)propan-2-amine will turn out to be like inferior versions of methylone & MDMA. As we proved with the 2-carbon ketone analogues of 2CB still have 5HT2a activity. That last one was a French idea...
Dresden
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Feb 2, 2010
- Messages
- 3,212
I like D. Maybe add a furanyl chlorine, though?
FOUR TWEENIUS
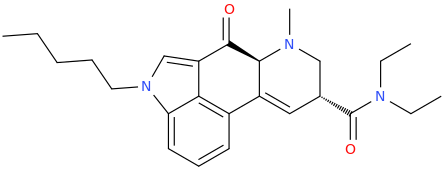
ANANDA
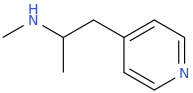
OSIRIS
Great CEVs.
Ah, The Joy Of A Well Placed Propane Pharmacophore!
It's Only Right That You Pay Homage To The Stuff That's About To Blow Up Your Nose. So Just Get On The Floor, And DANCE ALL NIGHT.
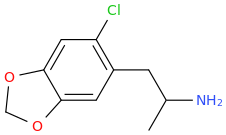
HONDA
Remember, this thread is a "joke." Or Not!

FOUR TWEENIUS

ANANDA

OSIRIS
Great CEVs.
Ah, The Joy Of A Well Placed Propane Pharmacophore!
It's Only Right That You Pay Homage To The Stuff That's About To Blow Up Your Nose. So Just Get On The Floor, And DANCE ALL NIGHT.

HONDA
Remember, this thread is a "joke." Or Not!
Last edited by a moderator:
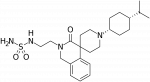
A bifunctional nociceptin and mu opioid receptor agonist is analgesic without opioid side effects in nonhuman primates
Corresponding authors: Nurulain T. Zaveri (Astraea Therapeutics, Mountain View, United States) and Mei-Chuan Ko (Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, United States)
Science Translational Medicine 2018, Volume 10, Issue 456, Page eaar3483
Published online August 29th, 2018
https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aar3483
Corresponding authors: Nurulain T. Zaveri (Astraea Therapeutics, Mountain View, United States) and Mei-Chuan Ko (Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, United States)
Science Translational Medicine 2018, Volume 10, Issue 456, Page eaar3483
Published online August 29th, 2018
https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aar3483
AT-121:Misuse of prescription opioids, opioid addiction, and overdose underscore the urgent need for developing addiction-free effective medications for treating severe pain. Mu opioid peptide (MOP) receptor agonists provide very effective pain relief. However, severe side effects limit their use in the clinical setting. Agonists of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptor have been shown to modulate the antinociceptive and reinforcing effects of MOP agonists. We report the discovery and development of a bifunctional NOP/MOP receptor agonist, AT-121, which has partial agonist activity at both NOP and MOP receptors. AT-121 suppressed oxycodone's reinforcing effects and exerted morphine-like analgesic effects in nonhuman primates. AT-121 treatment did not induce side effects commonly associated with opioids, such as respiratory depression, abuse potential, opioid-induced hyperalgesia, and physical dependence. Our results in nonhuman primates suggest that bifunctional NOP/MOP agonists with the appropriate balance of NOP and MOP agonist activity may provide a dual therapeutic action for safe and effective pain relief and treating prescription opioid abuse.

Last edited:
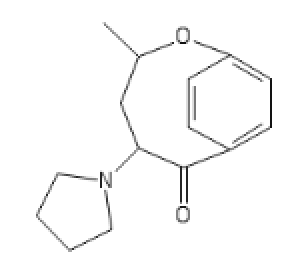
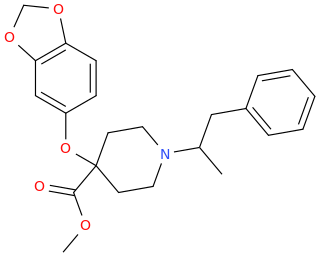
Dresden has come up with a dew things I actually searched for in Reaxys. Swapping a benzene for an 5-membered O or S containing ring seemed to require the O/S to be ortho - but that doesn't mean that they aren't active. Now, after uncovering 3-(dimethylamino)-2,2-dimethyl-1-phenylpropan-1-one in the 'Annual Report in Medicinal Chemistry (along with nexeridine and a few others), I tried running 3DQSAR data comparing 3,3-dimethyl prodine (ref on here somewhere) and no surprises, it overlays. Then I replaced one of the N-methyl with a 2-phenylethyl moiety and discovered that it overlaid PEPAP. So :
2,2-dimethyl-3-[methyl(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1-phenylpropan-1-one
I commend others to reproduce the results in CHARMM, ChemOffice or similar. Now, the prodine derivative is chiral and while one is x9 M, the other is inactive. Cunningly, in this case, the compound is achiral and far enough, the parent is equipotent. So I'm not going to claim huge activity - likely and order of magnitude higher than M but as you chemists will have noted, it's a single step synthesis. Now I suspect that like related compounds, it causes serious respiratory depression BUT on the plus side, duration is likely to be longer than pethidine or prodine (no ester) so N-demethylation seems the most likely fate.
2,2-dimethyl-3-[methyl(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1-phenylpropan-1-one
I commend others to reproduce the results in CHARMM, ChemOffice or similar. Now, the prodine derivative is chiral and while one is x9 M, the other is inactive. Cunningly, in this case, the compound is achiral and far enough, the parent is equipotent. So I'm not going to claim huge activity - likely and order of magnitude higher than M but as you chemists will have noted, it's a single step synthesis. Now I suspect that like related compounds, it causes serious respiratory depression BUT on the plus side, duration is likely to be longer than pethidine or prodine (no ester) so N-demethylation seems the most likely fate.
sekio
Bluelight Crew
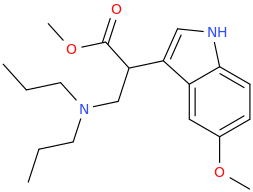
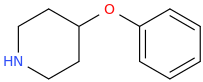
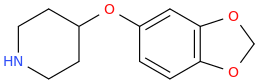
Re: the phenyl ether of piperidinol, apparently the phenyl ether of tropinol is an active stimulant.
sekio
Bluelight Crew
OK, I'll bite.
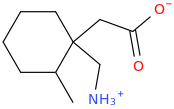
Overlays with leucine quite well...

Overlays with leucine quite well...
- Status
- Not open for further replies.