mr peabody
Bluelight Crew

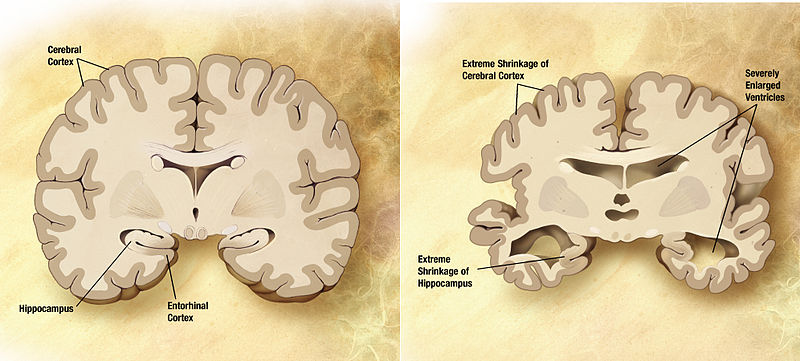
In vivo evidence of therapeutic properties of CBD for Alzheimer's Disease
A review and summary of animal subject studies of CBD in relation to neuroprotective effects and Alzheimer's disease. The studies demonstrate the ability of CBD to reduce the change caused by damage to neural cells and reduce the neuroinflammatory response. CBD was also shown to promote neurogenesis. Importantly, CBD also reverses and prevents the development of cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's rodent models. Interestingly, combination therapies (of CBD and THC) showed that CBD can antagonize the psychoactive effects associated with THC and possibly mediate greater therapeutic benefits than either phytocannabinoid alone.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5289988/
---
CBD modulates the expression of Alzheimer's Disease-related genes
Stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells to be exact, have emerged as a promising tool for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease. Current therapies for Alzheimer's that utilize mesenchymal stem cells have shown limited effectiveness. This study evaluates whether pre-treatment with cannabidiol modulates mesenchymal stem cells in order to improve their therapeutic potential. The results showed that pre-treatment with CBD prevented the expression of proteins and suggested that mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with CBD possess a molecular profile that might be more beneficial for the treatment of Alzheimer's.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28025562
---
Safety and efficacy of CBD for behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
With a given premise of THC as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's, this clinical trial looked at whether CBD oil was effective in relieving behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. CBD oil was given in addition pharmaceutical drugs already prescribed for this group of 11 trial participants. The trial lasted for 4 weeks. Results showed that delusions, agitation/aggression, irritability, apathy, sleep distress and caregiver distress were all reduced.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26757043
---
Cannabinoids for the treatment of agitation and aggression in Alzheimer's Disease
Utilizing the endocannabinoid system and synthetic cannabinoids for the modulation of neuroinflammation that is related to Alzheimer's disease was a given for this review. They looked at many studies, case studies and trials. Findings from 6 studies showed significant benefits from synthetic cannabinoids, specifically dronabinol and nabilone. It was noted that conclusions were limited by small sample sizes, short trial duration, and lack of placebo control in some of these studies.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26271310
---
CBD and other cannabinoids reduce microglial activation in Alzheimer's Disease
This study suggests that microglial activity has been shown as a feature of Alzheimer's disease. In the present study, they compared the effects of cannbidiol with those of other cannabinoids on microglial cell functions, learning behavior and cytokine expression after beta amyloid administration in mice. The study found that CBD was able to modulate microglial activity, and produce beneficial effects in animal subjects model of Alzheimer's.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21350020
---
CBD in vivo blunts meta-amyloid-induced neuroinflammation
To confirm the results of a previous study showing that cannabidiol inhibited gliosis in vivo in mice, mice were inoculated with human peptide into the right dorsal hippocampus, and treated daily with CBD and a non-CBD substance for 7 days. The dosage of CBD used was 2.5 or 10 mg per kg of body weight. CBD significantly inhibited markers of neuroinflammation in the animal subjects. This was also dose dependent. The results of this study confirm the in vivo anti-inflammatory actions of CBD.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17592514
---
Neuroprotective effect of CBD on Beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells
This study looked at the effect of cannabidiol on peptide toxicity in rat cells in culture. The toxic effect was increased reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation, cell death signaling cascade, increased intracellular calcium, and DNA fragmentation. Treatment of the cells with cannabidiol prior to toxic peptide exposure significantly elevated cell survival while it decreased reactive oxygen species production, lipid peroxidation, cell death signaling levels, DNA fragmentation and intracellular calcium. Results indicated that CBD exerts a combination of neuroprotective, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic (anti cell death) effects against peptide toxicity.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15030397
---
CBD reverses deficits in hippocampal LTP in a model of Alzheimer's Disease
Synaptic plasticity protection by cannabidiol is demonstrated for the first time in an in vitro model. The study looked at the effect of CBD on amyloid peptides. Amyloid peptides are known to reduce persistent increase in synaptic strength in the hippocampus part of the brain. CBD alone did not alter persistent increase in synaptic strength in the hippocampus. But, pre-treatment with CBD protected the persistent increase in synaptic strength. Essentially, CBD protected the hippocampus and memory from the peptide that is known to cause Alzheimer's disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29574668
.
Last edited: