-
N&PD Moderators: Skorpio | thegreenhand
-
Neuroscience & Pharmacology Discussion Welcome Guest
Posting Rules Bluelight Rules Recent Journal Articles Chemistry Mega-Thread FREE Chemistry Databases! Self-Education Guide
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Possible dopamineric neurotoxic effects of alcohol caused by salsolinol?
- Thread starter Amml
- Start date
asecin
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Apr 13, 2005
- Messages
- 1,725
IIRC the strongest MAOI compound in Rhodiola rosea extract, rosavin, only has an affinity of about ~10 uM ( = 4.28 microgram / mL = 4.28 milligrams / liter), comparable to piperine from black pepper. When you factor in that rosavin is a molecule consisting mostly by mass of polar sugar groups, its hydrophilic nature will mean it has difficulty penetrating into any fatty tissues (or through BBB w/o active transport) and is likely going to be subject to extensive metabolism too (lots of enzymes in the body work to pull sugar groups off of each other and smaller molecules, both of which would lead to inactivation of rosavin) I would imagine that any pharmacological effects of Rhodiola ext. are unlikely to be mediated by MAOI alone...
rosavin is the most studied part of rhodiola and it is claimed to cause its pharmacological action but that is false. the whole extract, containing perhaps dozen of various substances (most of which are not studied) is what works in synergy WITH rosavin to bring in its effect in action. as mentioned by you -lots of enzymes in the body work to pull sugar groups off of each other and smaller molecules, both of which would lead to inactivation of rosavin - which tells me you disregard the whole herb and all of its other dozen substances it contains that, perhaps, do inhibit these enzymes and the breakdown of rosavin or perhaps create different metabolites of rosavin and do create some activity. but i just checked studies on its MAOI activities and i see its COMT inhibitor, now im confused as to how COMT inhibition relates to MAOI inhibition?
COMT and MAO are both enzymes that break down catelochamines (Dopamin, Adrenaline), afaik COMT can't break down Tryptamines (Serotonin) such as MAO. They are different enzymes and again afaik they don't interact with each other directly. Maybe when COMT is inhibited more MAO is produced - same or higher katelochamin levels (Dopamine, Noradrenaline), but lower Tryptamine levels (Serotonin)? Idk
It is actually 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine that you are thinking of. It is taken up by SERT into serotonergic terminals and then causes oxidative stress.
No, i mean the condensation product between serotonin itself and acetaldehyde.
Indole is more electron-rich than benzene ring system thus this should be even more favorable than dopamine.
(In additional, this reaction is used in real organic synthesis of the harmala alkaloids)
Any study pointing to similar seretonergic toxicity of it?
Here are the images of serotonin + acetaldehyde Pictet-Spengler condensation products:
I am focusing on the left molecule.
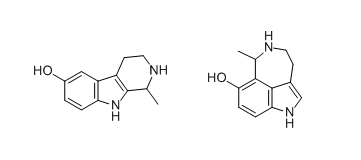
The structure looks very similar to beta-carbolines hamala alkaloids, but those have -OMe instead of -OH,
and the position is 6-, unlike 5- of this one.
serotonin2A
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Sep 13, 2014
- Messages
- 1,354
I was replying to the post by Amml -- it had nothing to do with your post.No, i mean the condensation product between serotonin itself and acetaldehyde.
Indole is more electron-rich than benzene ring system thus this should be even more favorable than dopamine.
(In additional, this reaction is used in real organic synthesis of the harmala alkaloids)
Any study pointing to similar seretonergic toxicity of it?
Here are the images of serotonin + acetaldehyde Pictet-Spengler condensation products:
I am focusing on the left molecule.

The structure looks very similar to beta-carbolines hamala alkaloids, but those have -OMe instead of -OH,
and the position is 6-, unlike 5- of this one.
No, i mean the condensation product between serotonin itself and acetaldehyde.
Indole is more electron-rich than benzene ring system thus this should be even more favorable than dopamine.
(In additional, this reaction is used in real organic synthesis of the harmala alkaloids)
Any study pointing to similar seretonergic toxicity of it?
Here are the images of serotonin + acetaldehyde Pictet-Spengler condensation products:
I am focusing on the left molecule.

The structure looks very similar to beta-carbolines hamala alkaloids, but those have -OMe instead of -OH,
and the position is 6-, unlike 5- of this one.
Phew, possible could be MAO-inhibition or specific 5-HT Receptor binding. For example Psilocin has a hydroxy group on C4, Serotonin has it on the C5, but I have no clue what this additional ring causes. It has the same structure as in Salsolinol, but still not TWO Hydroxy-groups like Salsolinol or 5,7-dihydroxy-tryptamine, I think the neurotoxic effects are mostly caused by the combination of the hydroxy-groups and the quinone. There are some papers about the possible routes of neurotoxicity of those substances.
If someone has more information on it feel free to post.
Last edited:
serotonin2A
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Sep 13, 2014
- Messages
- 1,354
The neurotoxicity is definitely due to the quinone. If you leave an aq. solution of 5,7-DHT at room temperature without an antioxidant then in short order it will oxidize to a blue color. Serotonergic neurons actually turn light blue after exposure because they concentrate the DHT and its oxidation products.Phew, possible could be MAO-inhibition or specific 5-HT Receptor binding. For example Psilocin has a hydroxy group on C6 too, Serotonin has it on the C5, but I have no clue what this additional ring causes. It has the same structure as in Salsolinol, but still not TWO Hydroxy-groups like Salsolinol or 5,7-dihydroxy-tryptamine, I think the neurotoxic effects are mostly caused by the combination of the hydroxy-groups and the quinone. There are some papers about the possible routes of neurotoxicity of those substances.
If someone has more information on it feel free to post.
The neurotoxicity is definitely due to the quinone. If you leave an aq. solution of 5,7-DHT at room temperature without an antioxidant then in short order it will oxidize to a blue color. Serotonergic neurons actually turn light blue after exposure because they concentrate the DHT and its oxidation products.
And what is the exact reaction that happens when Serotonin is oxidized? Is just the Hydroxy-group transformed to a double bound oxygen? That wouldn't be a quinone right? But two double bound Oxygen on a Benzene are a quinone? Is that the reason why 5,7-DHT is neurotoxic?
Edit: Sorry understood that wrong, though you meant when normal serotonergic neurons are exposured to air.
@pomazazed: Actually the Pictet-Spingler reaction between serotonin and acetaldehyde to form 2-methyl tetrahydro beta-carboline is as likely (if not more likely) to take place than between dopamine and acetaldehyde. Because as you mentioned the indole of serotonin is as activated as the catechol of dopamine. So everything else being equal, if the alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde in the brain reacts with DA, there is not reason why it can't react with 5HT. But of course you'll have to suppose same brain concentration and distribution of 5HT and DA so that both can compete with the aldehyde. But I am not sure the brain distribution of the alcohol dehydrogenase metabolizing ethanol to acetaldehyde: that can make a difference whether that happens in dopaminergic neurons to give salsinol tetrahydroquinoline more or in serotonergic neurons to give harmalines (I dont know how to explain that but I guess you get the point)
Neo-natal rats brain exposed to ethanol will metabolize Serotonin into beta-carboline among other metabolic pathways .. with pretty dire brain developmental consequences actually!! (later on that) : (how relevant this is with drunk humans.. or pregnant women drinking who knows?
[Determination of 6-hydroxy-1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-beta-carboline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid in the neonatal rat brains using high performance iquid chromatography-electrochemical detection].
Neo-natal rats brain exposed to ethanol will metabolize Serotonin into beta-carboline among other metabolic pathways .. with pretty dire brain developmental consequences actually!! (later on that) : (how relevant this is with drunk humans.. or pregnant women drinking who knows?
[Determination of 6-hydroxy-1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-beta-carboline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid in the neonatal rat brains using high performance iquid chromatography-electrochemical detection].
Last edited:
Cotcha Yankinov
Bluelight Crew
- Joined
- Jul 21, 2015
- Messages
- 2,952
So this means that actually substances that wouldn't cross the BBB could get into protected brain regions over those unprotected brain areas?
AFAIK oral GABA supplementation has actually no CNS effects, other that 5-HTP
Sorry I didn't see this post; I don't think molecules are very good at diffusing through the brain so the BBB is probably pretty effective there, but I mentioned GABA because I remembered reading that there was a growth hormone response induced by peripheral GABA administration that seemed to be facilitated by the paraventricular nucleus.
Sorry I didn't see this post; I don't think molecules are very good at diffusing through the brain so the BBB is probably pretty effective there, but I mentioned GABA because I remembered reading that there was a growth hormone response induced by peripheral GABA administration that seemed to be facilitated by the paraventricular nucleus.
Ah interresting thanks
And what is the exact reaction that happens when Serotonin is oxidized? Is just the Hydroxy-group transformed to a double bound oxygen? That wouldn't be a quinone right? But two double bound Oxygen on a Benzene are a quinone?
Aerial Autoxidation with oxygen in air to form a hydroperoxide, which then spontaneously decompose to corresponding quinone at ortho-position to the original hydroxy group.
https://de.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salsolinol
It's only in German but it seemed right that significant amounts of Salsolinol are produced in the brain when ethanol is consumed and it's even responsible for a part of the effects of ethanol.
It's only in German but it seemed right that significant amounts of Salsolinol are produced in the brain when ethanol is consumed and it's even responsible for a part of the effects of ethanol.
