S.J.B.
Bluelight Crew
- Joined
- Jan 22, 2011
- Messages
- 6,886
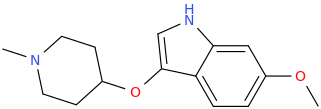
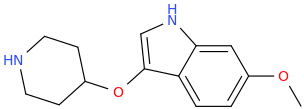
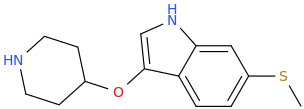
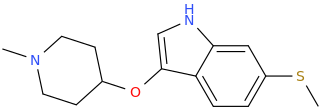
Synthetic Studies of Neoclerodane Diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Analogues with Improved Potency and G-protein Activation Bias at the μ-Opioid Receptor
Corresponding author: Thomas E. Prisinzano (Department of Medicinal Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, University of Kansas, Lawrence, United States)
ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2020, Volume 11, Issue 12, Pages 1781–1790
Published online May 8th, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00191

Corresponding author: Thomas E. Prisinzano (Department of Medicinal Chemistry, School of Pharmacy, University of Kansas, Lawrence, United States)
ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2020, Volume 11, Issue 12, Pages 1781–1790
Published online May 8th, 2020
https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00191
Previous structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies identified the first centrally acting, non-nitrogenous μ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonist, kurkinorin (1), derived from salvinorin A. In an effort to further probe the physiological effects induced upon activation of MORs with this nonmorphine scaffold, a variety of analogues were synthesized and evaluated in vitro for their ability to activate G-proteins and recruit β-arrestin-2 upon MOR activation. Through these studies, compounds that are potent agonists at MORs and either biased toward β-arrestin-2 recruitment or biased toward G-protein activation have been identified. One such compound, 25, has potent activity and selectivity at the MOR over KOR with bias for G-protein activation. Impressively, 25 is over 100× more potent than morphine and over 5× more potent than fentanyl in vitro and elicits antinociception with limited tolerance development in vivo. This is especially significant given that 25 lacks a basic nitrogen and other ionizable groups present in other opioid ligand classes.