izo
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Mar 22, 2006
- Messages
- 4,165
next profile, well known:

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
an extra wiki site for the alkaloids:

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
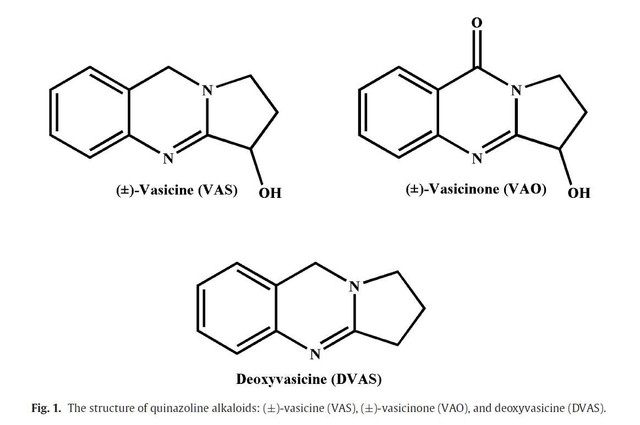
ingredients on wiki:
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
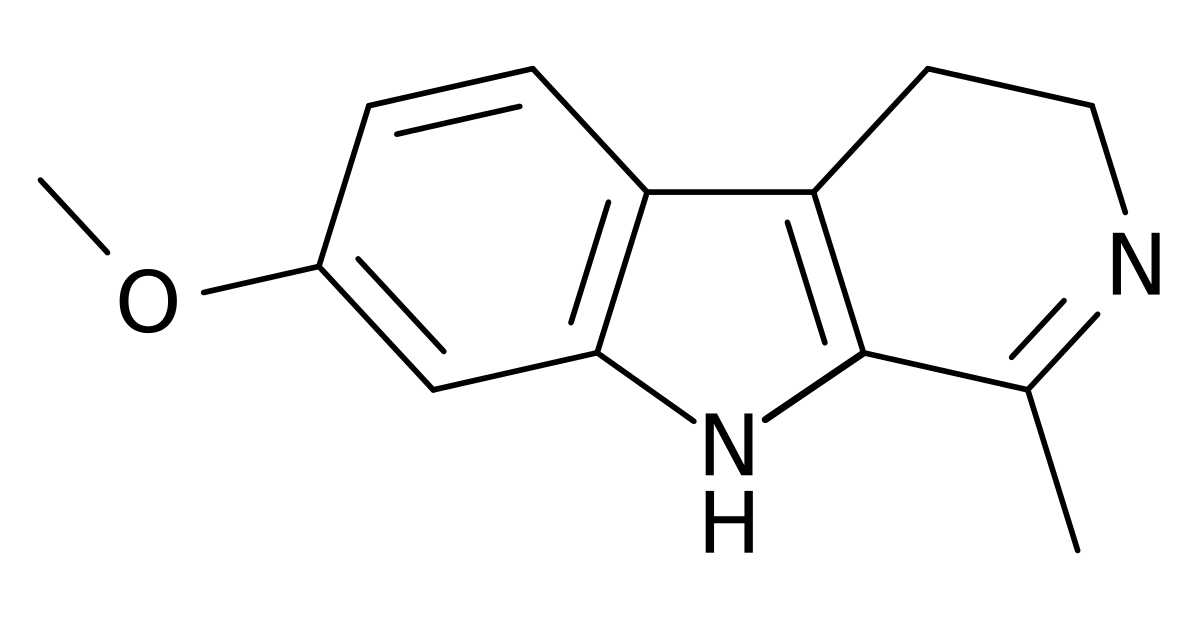
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
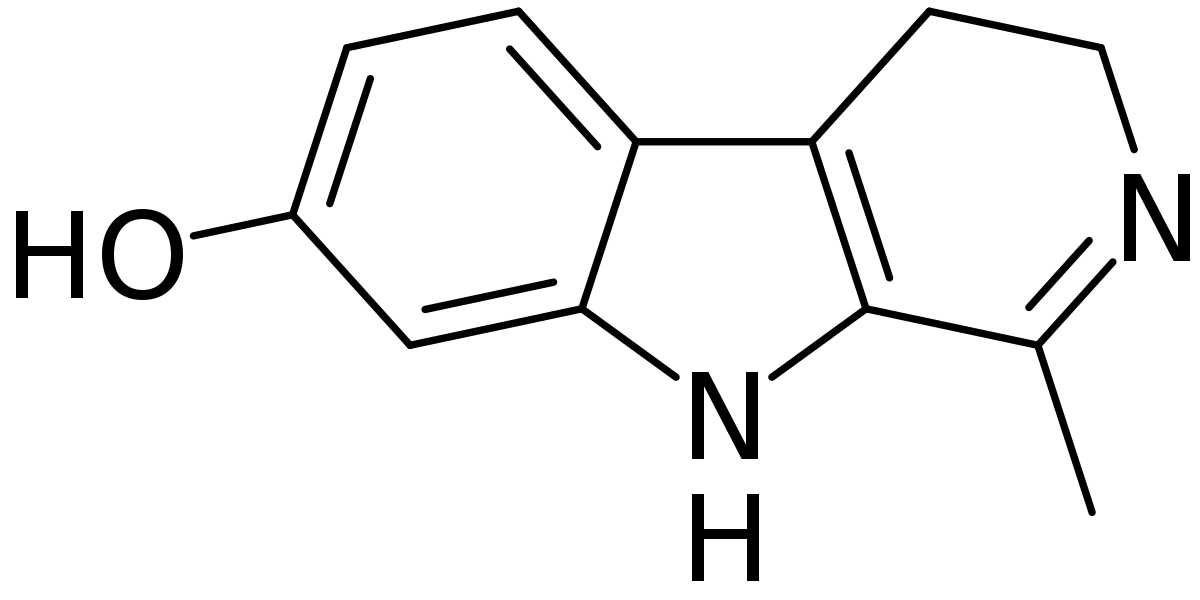
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
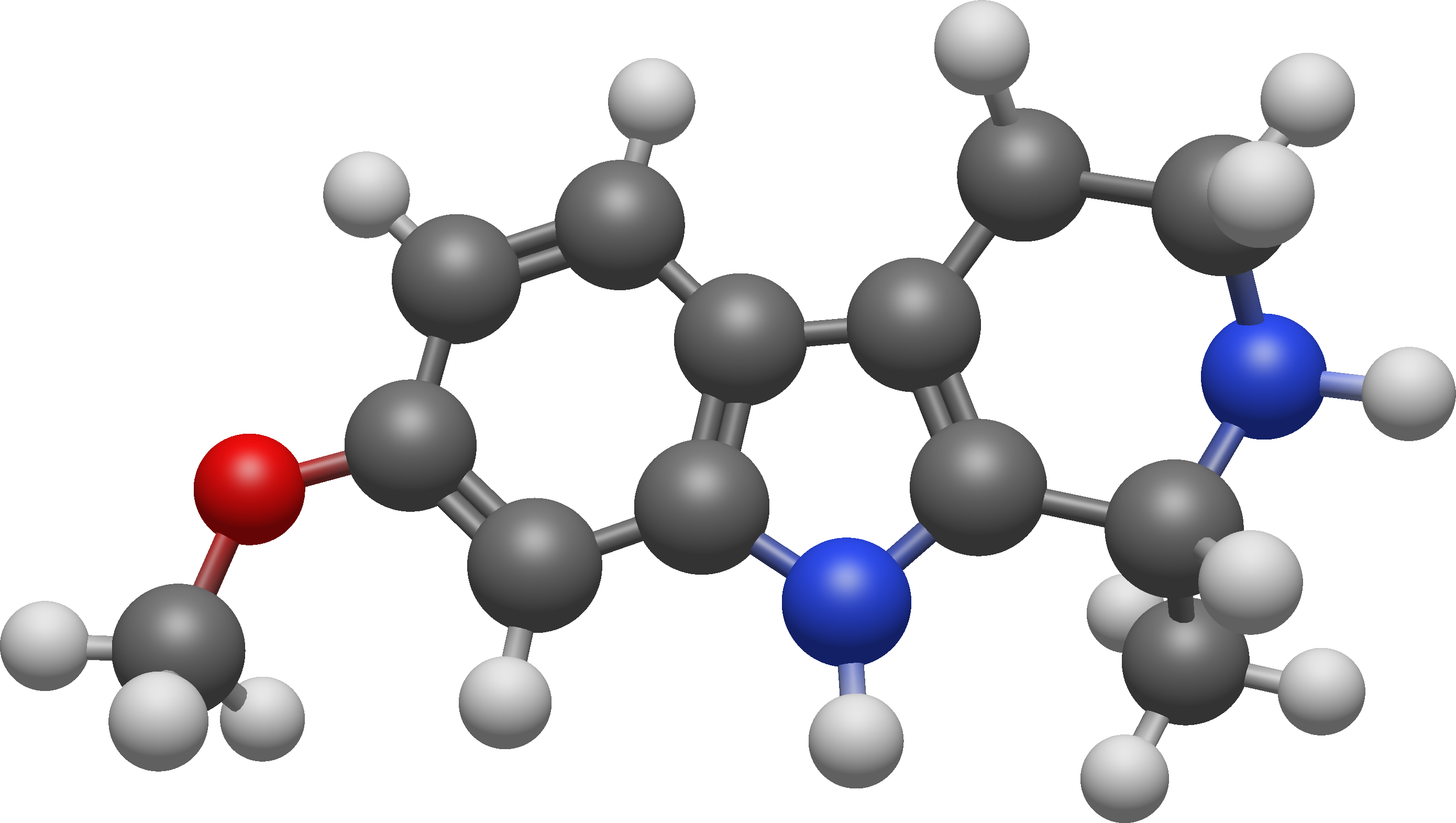
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
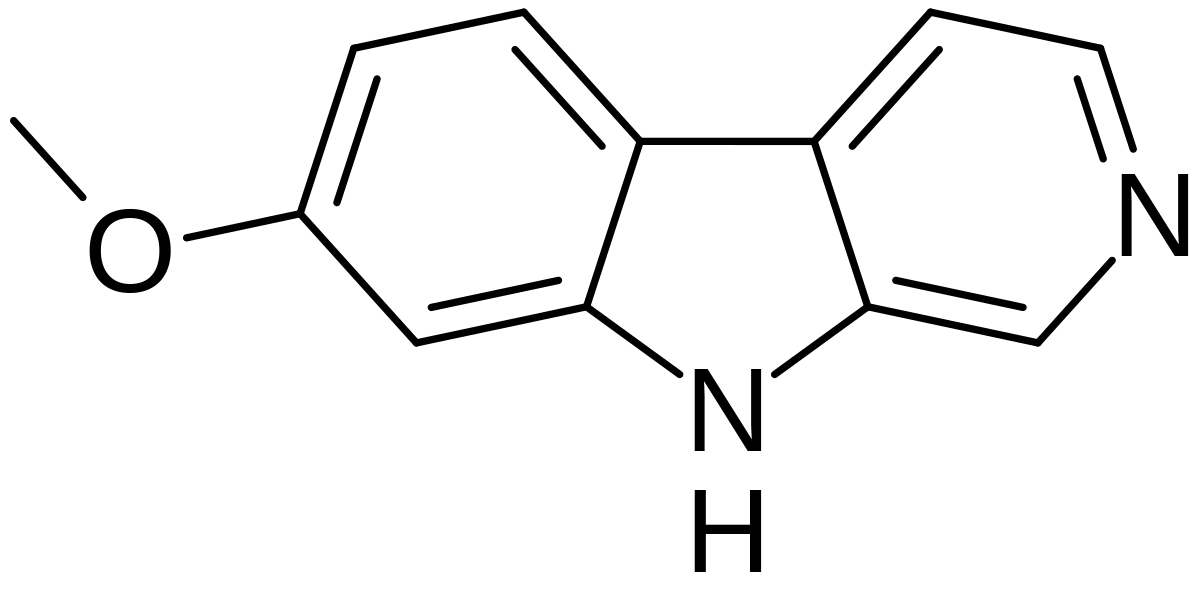
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
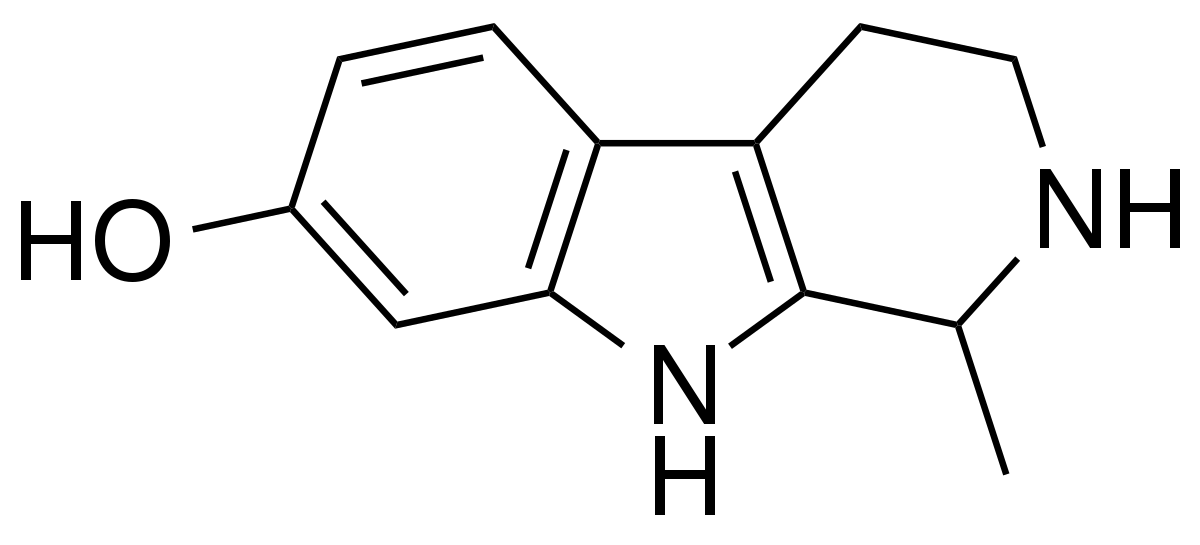
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org

Peganum harmala - Wikipedia
an extra wiki site for the alkaloids:

Harmala alkaloid - Wikipedia
ingredients on wiki:
Harmine - Wikipedia

Harmaline - Wikipedia

Harmalol - Wikipedia

Tetrahydroharmine - Wikipedia

Norharmine - Wikipedia