AlsoTapered
Bluelighter
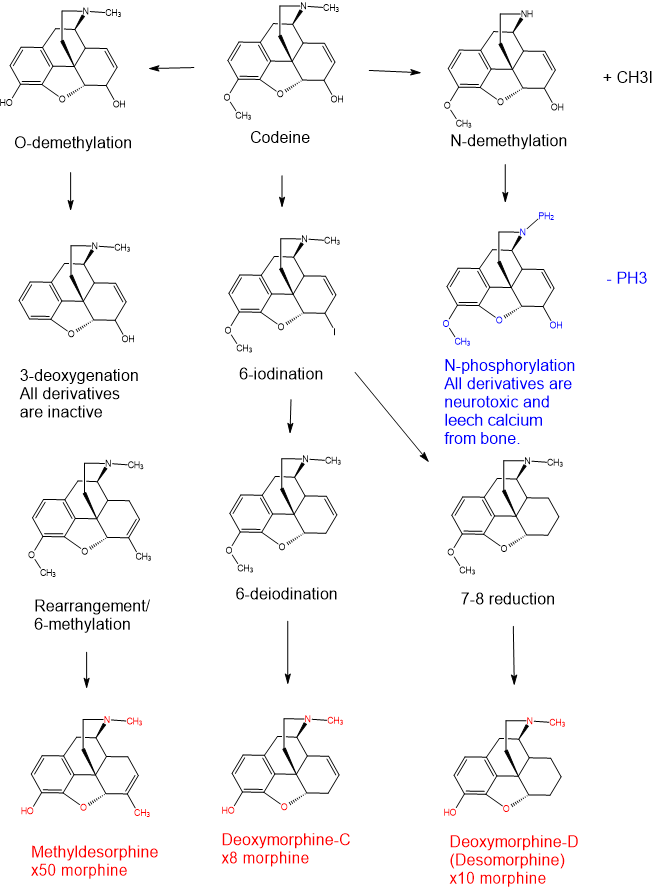
It was not possible to show EVERY intermediate but I have shown the five major points of the scaffolds that undergo modification .i.e.
1 - 3-O-demethylation
2 - 3-deoxygenation
3 - 6-halogenation/dehalogenation
4 - 7-8 reduction
5 - allylic rearrangement and 6-methylation (underlying reaction as yet unknown)
The above image demonstrates most of the intermediates, reactions and toxic reagents/species found in Russian samples of 'krokodil' which isn't a pure compound but a number of actives, inactives and toxins. It's worth looking at the MSDS of CH3I (methyl iodide) and PH3 (phosphine) which are both volatile.
Put simply, phosphorous-containing species intecalanate into the morphinan converting the nor compounds into the coresponding phospinous amide. The KEY detail of phosphoramides is that they are incapable of forming addition salts with appropriate acids.
Similarly the non-selective nature of the reduction also results in the phenolic moiety being reduced (deoxygenated) and as a result the coresponding 3-desoxy species are incapable of forming addition salts with the appropriate bases.
Although the nor compounds are found in samples of krokodil and such compounds have been demonstrated to possess affinity for the MOR, most researchers believe that they do not readily cross the blood-brain barrier and so should considered inactive but non-toxic.
It's interesting (to me) that the CHI3 produced by the N-demethylation can itself react with iodocodeine/iodomorphine to produce the 6-methyl derivatives which are far more potent than the other actives. The 11 samples I have data on suggest yields of:
Deoxymorphine-D (Desomorphine) 21%-24%
Deoxymorphine-C 3%-6%
Methyldesorphine 2%-3.5%
It's important to note that the ULTIMATE fate of all the compounds if sufficient reagents and heating are applied is to undergo the 3-deoxygenation. While certain reactions only apply to intermediates, the various reactions are essentially happening in parallel and so the highest yields are achieved by understanding the optimal conditions (duration, temperature, ratio of reagents) and NOT simply by adding MORE of everything.
Having seen footage of one particularly skilled Russian 'cook', it's evident that some makers were aware of the toxic phosphoramides that are produced using the 'classic' methodology and I think it reasonable to state that avoiding the use of phosphorous greatly reduces the toxicity of the product.

The harmful chemistry behind krokodil (desomorphine) synthesis and mechanisms of toxicity
“Krokodil” is the street name for the homemade injectable mixture that has been used as a cheap substitute for heroin. Its use begun in Russia and Ukr…
Effects of krokodil (desomorphine) use on oral health - a systematic review - British Dental Journal
Introduction The narcotic drug krokodil is a semi-synthetic drug used as a cheap alternative to heroin. With its active ingredient desomorphine it is a highly addictive and destructive drug mainly used in Russia and Eastern Europe. Relatively little is known about the physical effects of...
Krokodil (Desomorphine)-induced osteonecrosis of the maxilla: a case report and literature review | Journal of Oral Medicine and Oral Surgery
Journal of Oral Medicine and Oral Surgery revue de la SFCO. Elle est consacrée à l étude et au traitement des affections de la cavité buccale, ainsi qu à la formation continue, à la recherche et aux progrès techniques et scientifiques

In vitro metabolism of desomorphine
Desomorphine is reported to be the principal pharmacologically active opioid in Krokodil, a homemade injectable drug that is perceived to be a cheaper…
A âKrokodilâ emerges from the murky waters of addiction. Abuse trends of an old drug
âKrokodilâ is the street name for the semi-synthetic opioid derivative desomorphine. Although an old drug, it re-staged on âdrug arenaâ during the lasâ¦

Breaking worse: The emergence of krokodil and excessive injuries among people who inject drugs in Eurasia
Krokodil, a homemade injectable opioid, gained its moniker from the excessive harms associated with its use, such as ulcerations, amputations and disc…
Last edited:



