izo
Bluelighter
- Joined
- Mar 22, 2006
- Messages
- 4,165
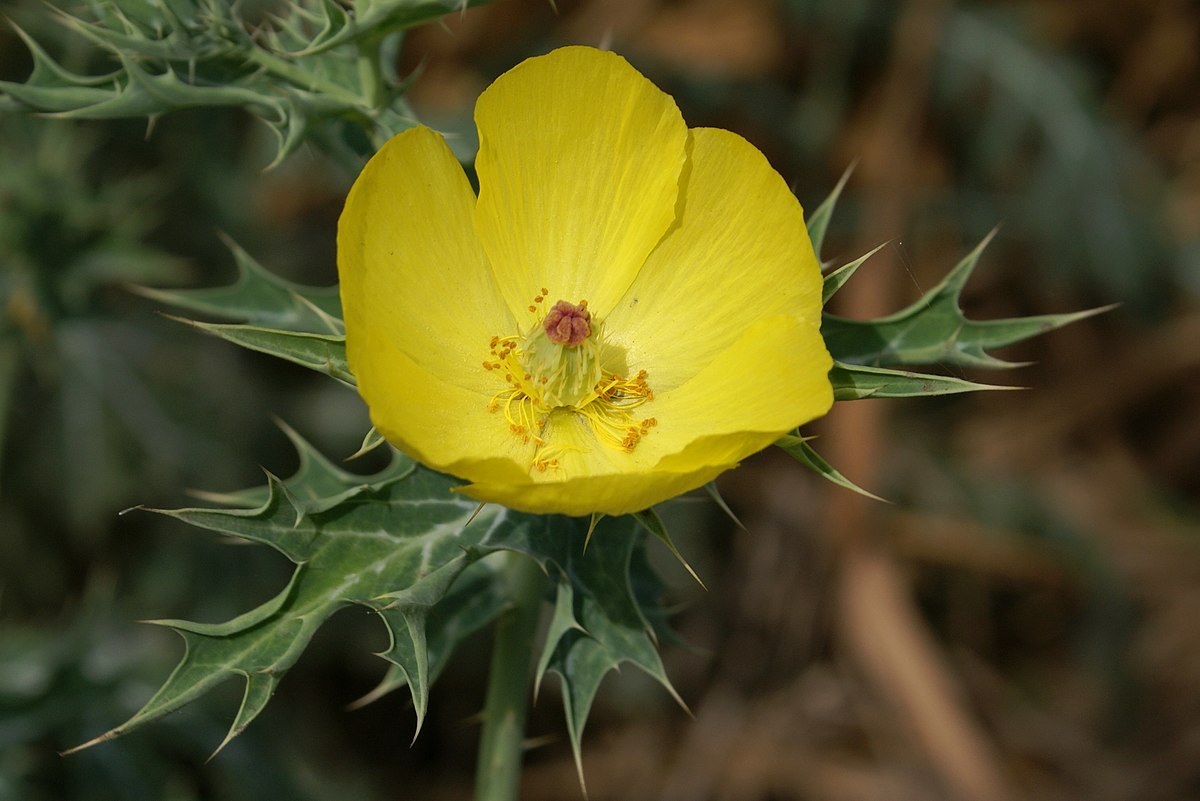
this one is also better known:

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
alkaloids on wiki:
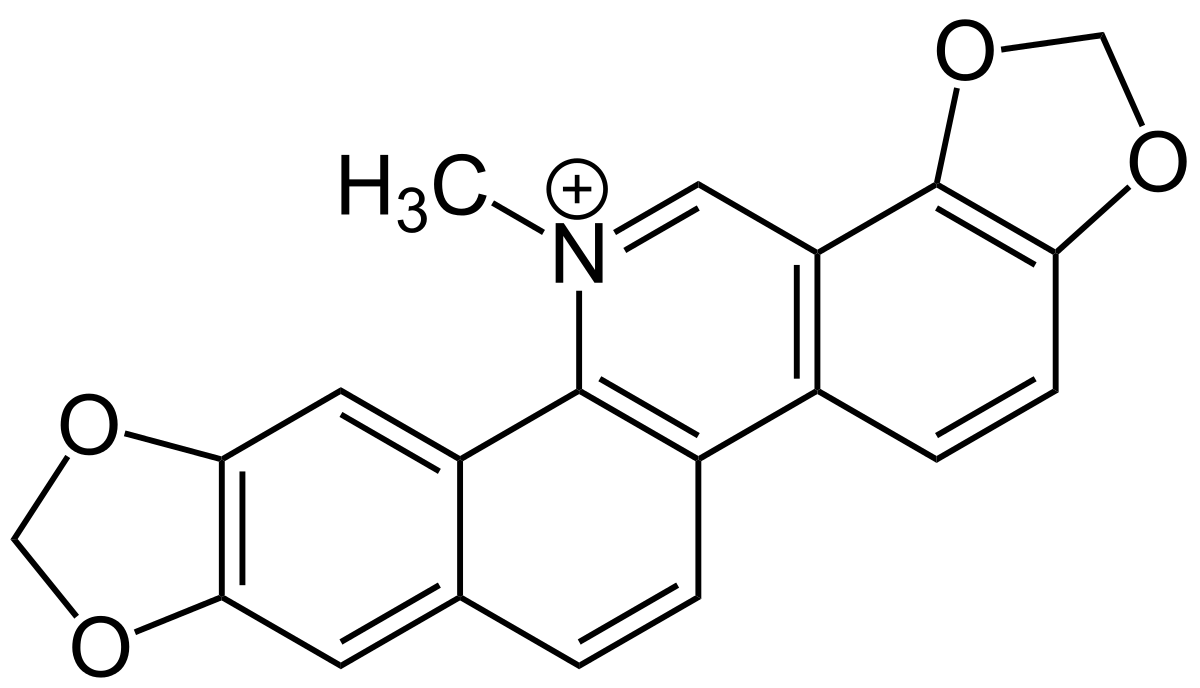
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
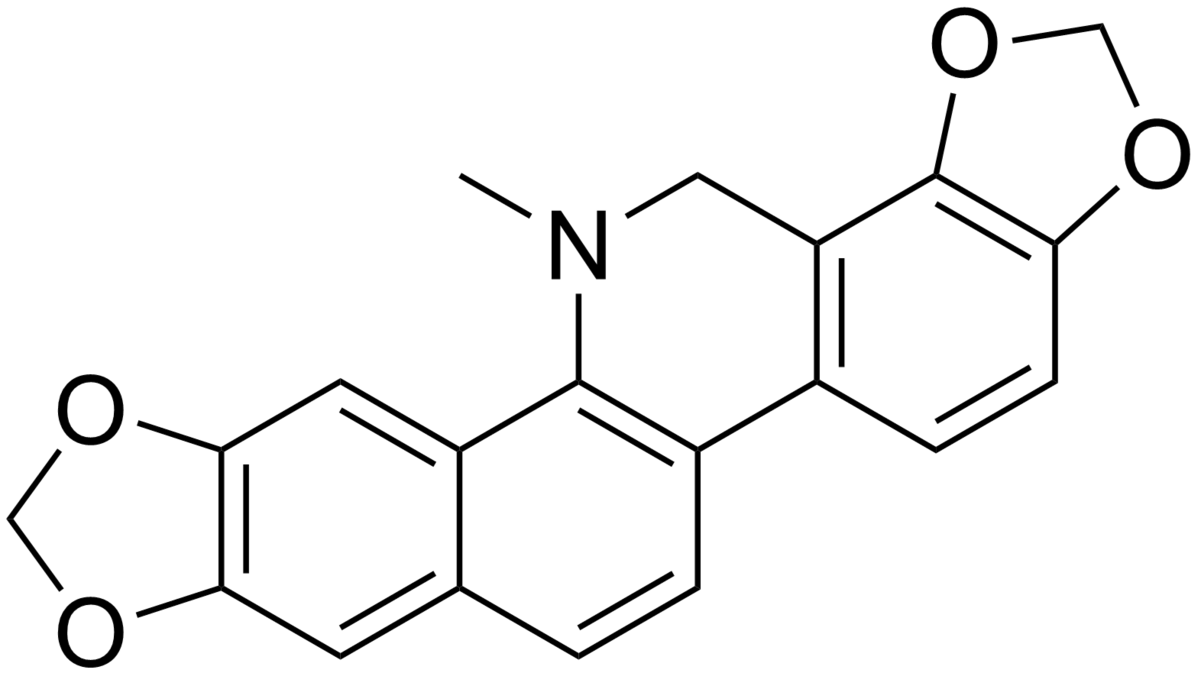
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
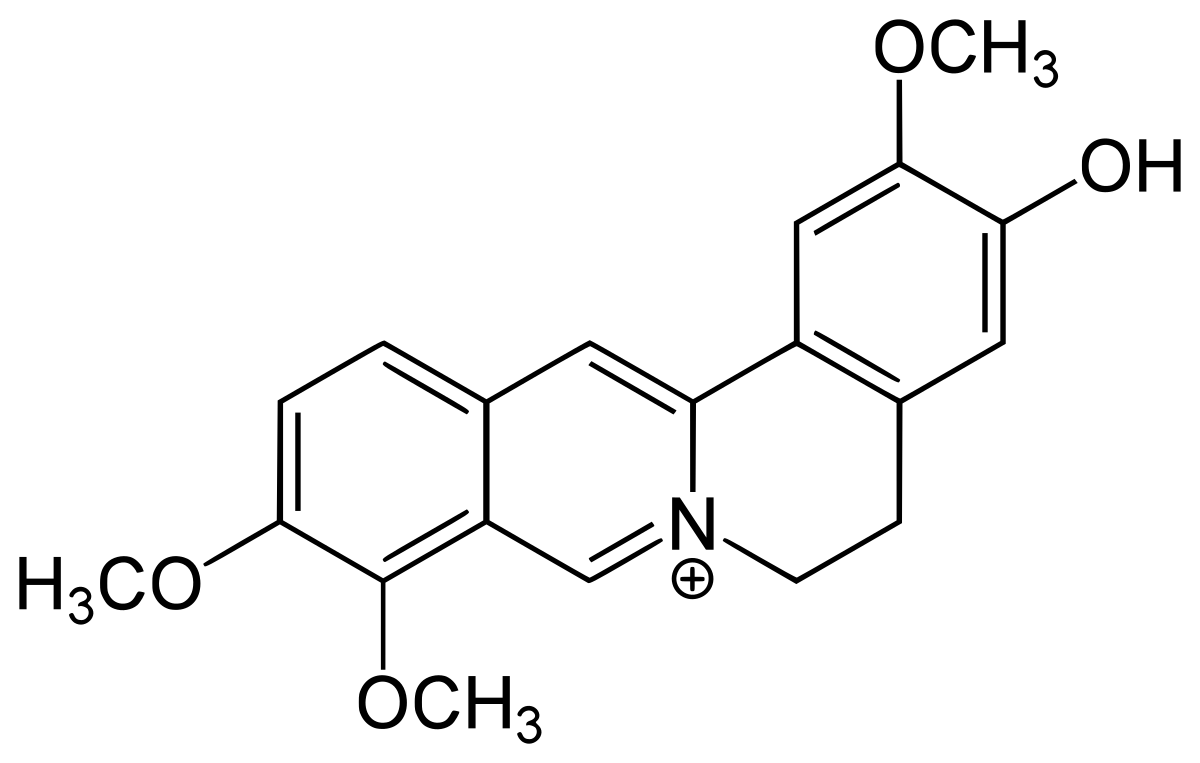
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
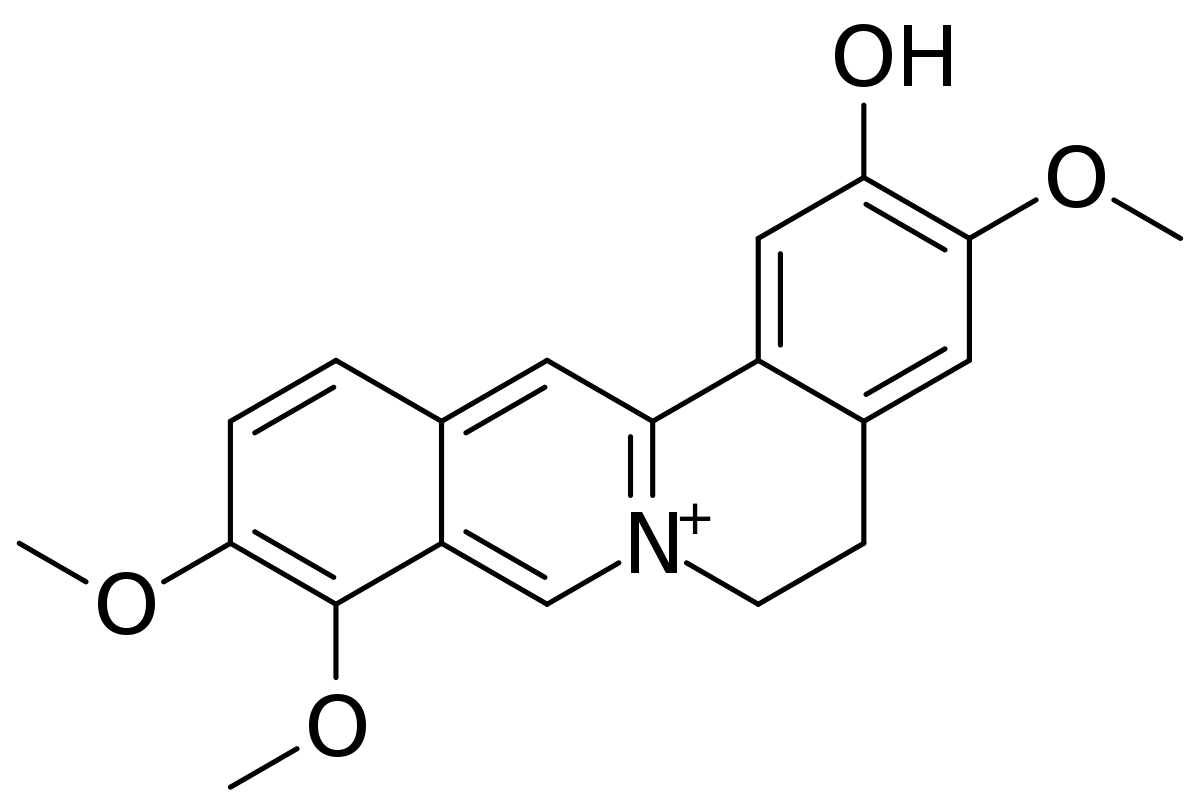
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
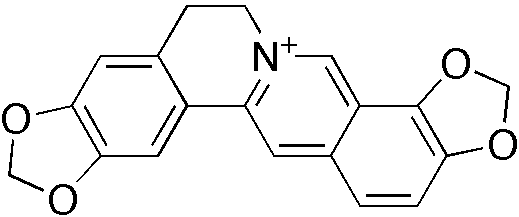
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
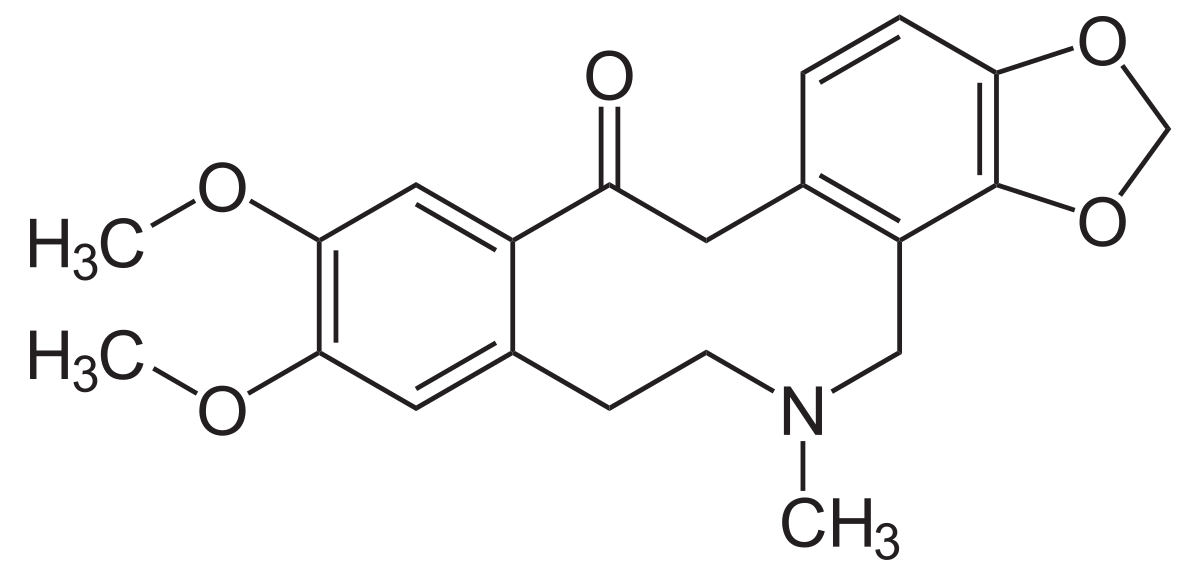
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
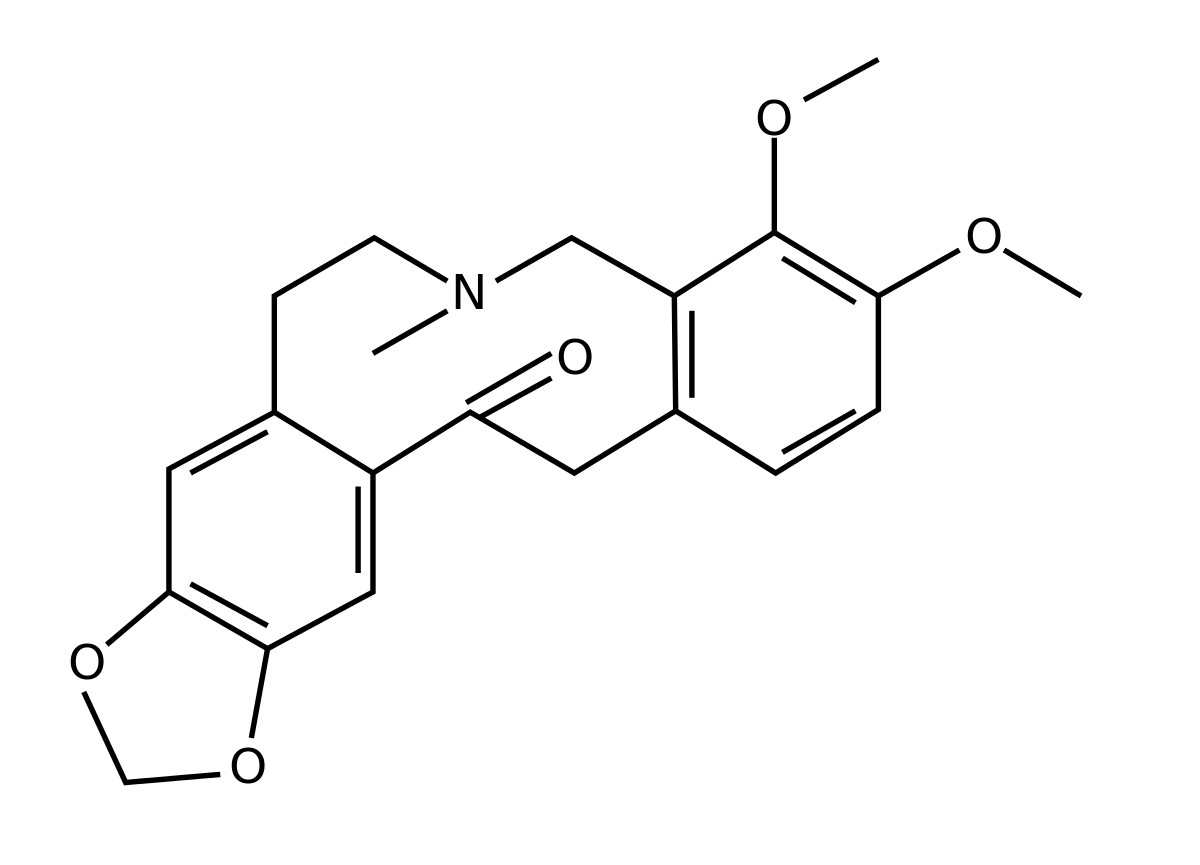
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
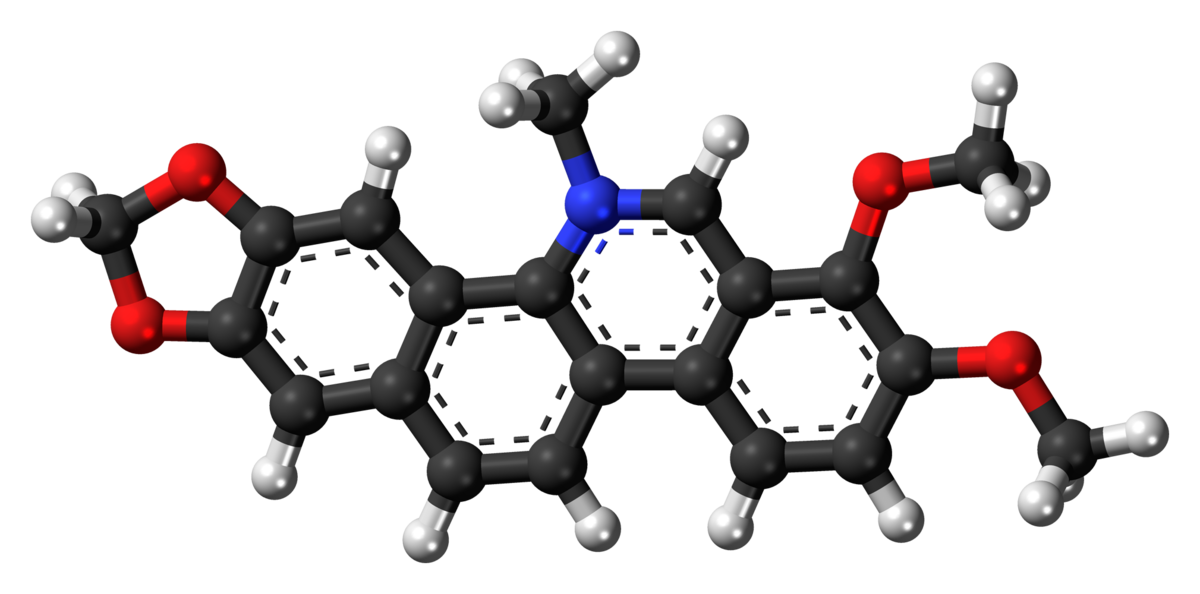
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
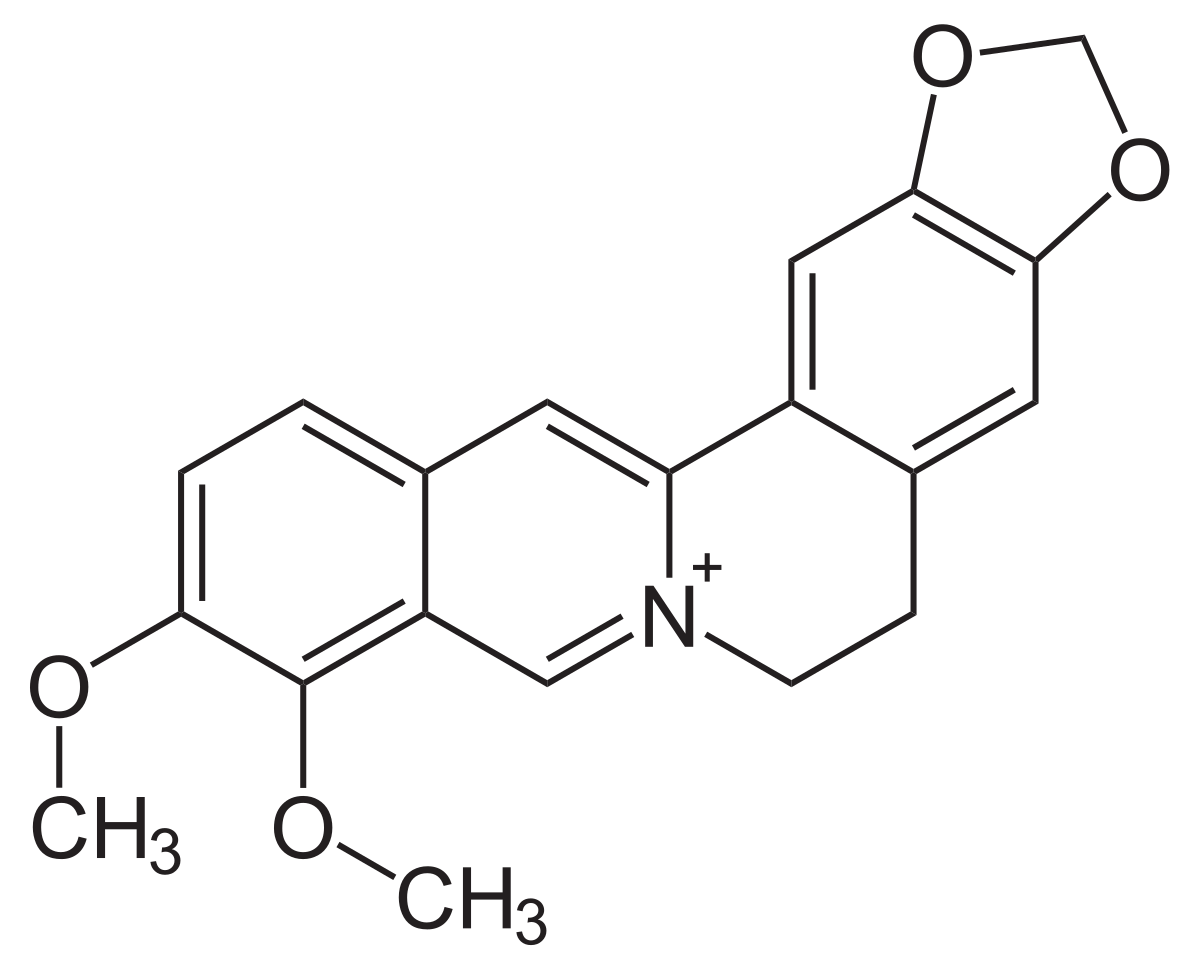
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
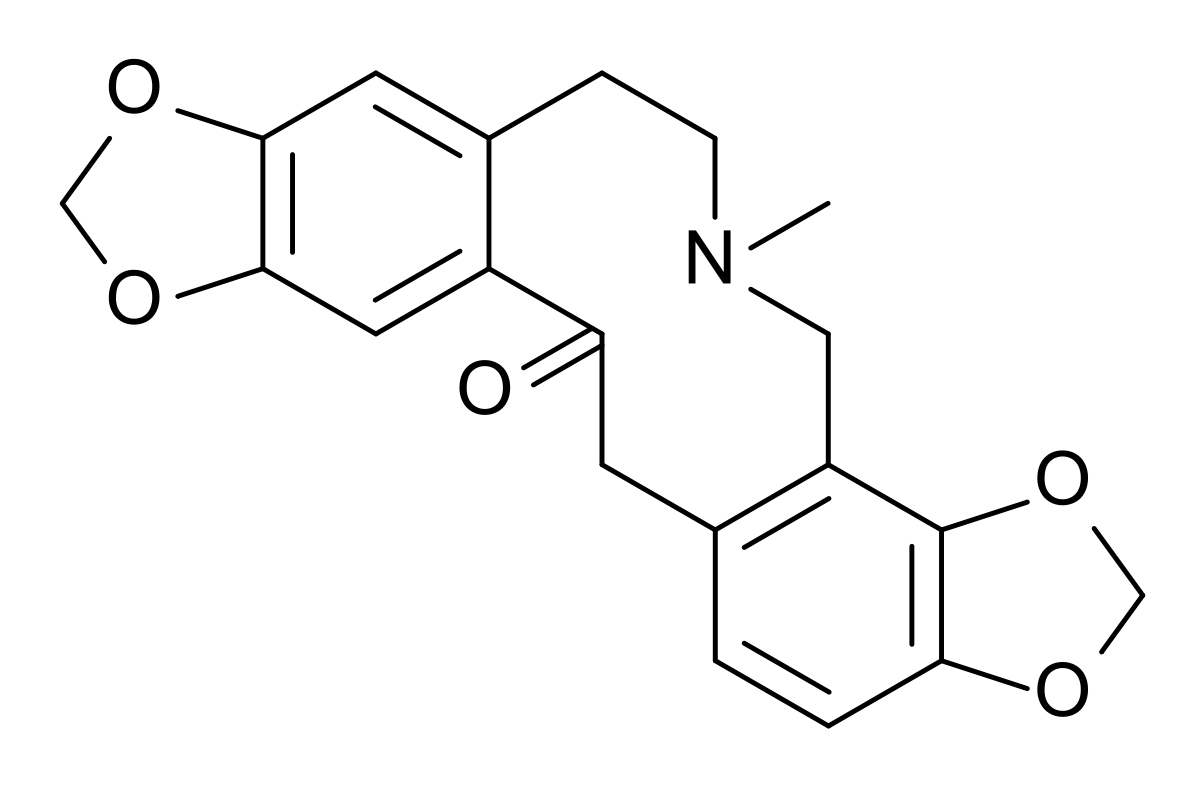
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org

Argemone mexicana - Wikipedia
is said to have an aphrodisiac, relaxing, euphoric and slightly analgesic effect.
alkaloids on wiki:

Sanguinarine - Wikipedia

Dihydrosanguinarine - Wikipedia

Jatrorrhizine - Wikipedia

Columbamine - Wikipedia

Coptisine - Wikipedia

Cryptopine - Wikipedia

Allocryptopine - Wikipedia

Chelerythrine - Wikipedia

Berberine - Wikipedia

